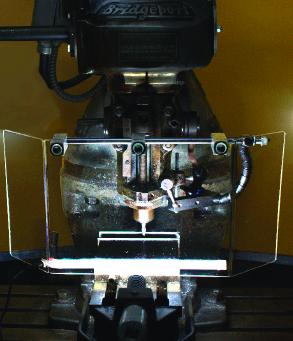
Flexbar Machine Corporation (Islandia, NY) introduces its new line of state-of-the-art Machine Safety Guards featuring Built-in LED Lighting providing machine operators with super bright illumination of the working field. The Visorguard-LED’s unique Continuous LED strip lighting is integrated as part of the safety shield providing 6000K natural white light with a 170 degree beam angle. Auto-Diffuse lighting produces no LED light hot spots.
Flexbar’s Visorguard-LED™ system is water and coolant proof and installs in minutes on CNC mills, conventional mills, drill presses and more. The adjustable Flexbar® arm permits setting of the Visorguard shield at the correct height and angle for each setup, then locks rigid. The special wing-shaped shield flips up to load a part and down for machining. A special spring-loaded shaft allows the shield to stay put with no spring back.
The built-in Visorguard-LED™ lighting is powered through a choice of two available system options:
- A compact 12V Rechargeable Battery Pack with on/off switch provides at least 4 hours of lighting per charge. It can be easily attached to side wing of the shield with included Velcro strips. 12V charger is also included.
- System can be powered through a 12V direct wire wall transformer with 8-foot cable and on/off switch.
Replacement Visorguard-LED™ shields and power kits are available for current Flexbar Visorguard users who can conveniently upgrade their current system to LED lighting.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- computer numerical control ( CNC)
computer numerical control ( CNC)
Microprocessor-based controller dedicated to a machine tool that permits the creation or modification of parts. Programmed numerical control activates the machine’s servos and spindle drives and controls the various machining operations. See DNC, direct numerical control; NC, numerical control.
- coolant
coolant
Fluid that reduces temperature buildup at the tool/workpiece interface during machining. Normally takes the form of a liquid such as soluble or chemical mixtures (semisynthetic, synthetic) but can be pressurized air or other gas. Because of water’s ability to absorb great quantities of heat, it is widely used as a coolant and vehicle for various cutting compounds, with the water-to-compound ratio varying with the machining task. See cutting fluid; semisynthetic cutting fluid; soluble-oil cutting fluid; synthetic cutting fluid.

