ToolRoom RN34 is the latest generation of ANCA’s successful software package that has been specially designed for the aerospace, die and mold, general machining and power generation industries.
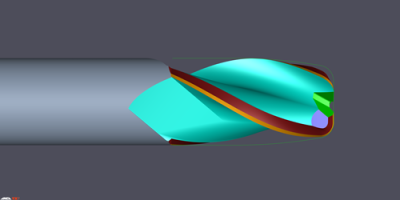
Thomson Mathew, ANCA software product manager, said: “ToolRoom RN34 is aimed to be the differentiator among many suppliers of endmill manufactures in the industry by allowing customers to design complex geometries through software to achieve increased tool life, productivity, cutting volume and increased quality and precision of the workpiece. The constant helix ballnose option, for example, is replaced by a graphical drag-and-drop designer. This ballnose type of tool, with optimised irregular helix curves to reduce vibration, and with near-instant visualisation easily achieved by switching from the 2D projection of the cutting edge to the 3D.”
The new software promises benefits of:
- Improved productivity through the intuitive creation of complex endmill geometries.
- Tool balancing to increase tool life, cutting volume, quality and precision of the workpieces.
- Minimising chatter through the simple design of high performance, complex tools.
Douglas Franke, Fraisa production manager, said: “with ANCA’s balancing software we have a tool balanced generally within five minutes. Some of our more complex tooling can take a little longer – up to 20 minutes. This drastically decreased our time in setup on the machine which could take several hours. Our biggest success story has been an aerospace customer who is running our 1” aluminium roughing tool at 25k rpm.”
ANCA's ToolRoom software provides industry renowned tool design flexibility, from the simplest to the most challenging tasks. With the benefit of over 40 years of grinding knowledge, ToolRoom supports both manufacturing or regrinding applications. Flexibility is further enhanced by the fact that ANCA develops all aspects of the machine in house - from the CNC system and application software to the machine and its accessories.
The new ballnose cycles allow end users to manufacture a range of ballnose tools suitable for finishing and roughing. The new designer edge can accommodate high helix on ball cutting edge for better fracture resistance and reduced vibration due to the irregular curve.
- Ballnose with designer cutting edge.
- New chisel edge grinding method.
- Curvature gash – curved gash surface.
- Flute gash – curved ball gash and fluting in single move.
- Facet gash with periphery of 1A1 or 1V1 wheels.
- Bullet and Bullnose style tools.
- 11V5 wheel grinding methods for improved wheel life.
- Square to ballnose blank roughing cycles.
- Various other methods of OD grinding with 11M2 wheels.
The double corner radius allows the design of barrel shape or lens shaped tools with larger to
smaller or smaller to larger radius from the end of tool. Vibration and deflection are reduced with
this style of geometry and the thinner chips that are formed provide longer tool life and enhanced
performance.
- Barrel shape – large radius to small towards the end of tool.
- Lens shape – small to larger radius towards the endface.
- Curved endface design.
- Roughing operation for corner radius tools.
Tool balancing is done on variable helix and pitch or single flute tools to minimise the eccentricweight distribution when using high speed machining. The benefits include reduced noiseand vibrations, improved machine bearing life, and better surface finish.
The different methods of balance are:
- Flute length extension
- Shank notch
- Support for the following option combinations:
- Variable helix with NAS hook
- NAS hook with radial land
- Variable helix and pitch with radial land
- Per–flute programming options to control flute length, flute depth, core taper etc. individually.
- Support for single flute tools to have depth equal or greater than tool radius.
- High helix angles for better surface finish and chip removal.
- Shear lollipop for deburring applications.
- Chip breakers for light work and the medical industry.
- Use of iView and LaserPlus for measurement and compensation.
- Ability to choose between forward and reverse infeed.
New operation in endmill cycles to add OD chipbreakers.
- Automatic or manual modes.
- Applicable to all straight OD profile to complement corner radius, ballnose, side and face cutters and endface operations. A library of all the ANCA supplied collet adaptors and collets are available for the user.
This adds additional functionality in allowing one TOM file to be embedded into another TOM file.
- Example: Corner radius with multi drill gash.
- Like the iPunch operation in iGrind and KHP.
- Some limitations exist, such as use of tool segments.
Support for a wide range of constant helix, constant lead and shear cutters widely used in the aerospace and power generation industries. All the above are supported for unmanned production with the support of the inbuilt LaserPlus which is fully automated.
- Support for constant helix fir tree cutters.
- Helical fluting with hook generating a flat flute surface.
- Support for iView and LaserPlus.
A new wizard style ToolType has been added for countersink tools to support standard flute and fan gash flute style. The new countersink flute operation can define special flute shapes required for this application.
- Support for RR, LL, RL, LR combinations.
- Relief grinding using step editor sections.
- Supports non-zero shear and upto 6 flutes.
- Automatic CIM3D blank form.
A new feature is added to OD backoff/raised land fluting operation for drills, to be able to produce second margin towards trailing edge of the tool.
- Double margin can be produced in both the backoff types OD and raised.
- The second margin can also float at an offset angle from cutting edge of the tool.
- This feature is made available to drills and step tools.
Manufacturing of a variety of threadmills is now possible with the addition of two new operations to the operations list. Threadmill grinding and cresting operations are supported with formed and standard fluting operations.
- Support for drill threadmill, straight OD, tapered OD and all the combinations.
- Possible to grind insert style or single rib threadmills.
- LaserPlus support for large volume production.
Pocket grinding software allows the user to quickly and easily define PCD pocket geometry. This is required for PCD tools used mainly in the woodworking and aerospace industries for composite and nonferrous materials.
- Ability to specify pocket geometry as common or for individual flutes.
- Position of pockets can be fixed or alternated based on number of flutes.
- Supported with spindle speed increaser hardware on all platforms for mounted point wheels.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- backoff
backoff
Rapid withdrawal of the tool from the workpiece.
- chatter
chatter
Condition of vibration involving the machine, workpiece and cutting tool. Once this condition arises, it is often self-sustaining until the problem is corrected. Chatter can be identified when lines or grooves appear at regular intervals in the workpiece. These lines or grooves are caused by the teeth of the cutter as they vibrate in and out of the workpiece and their spacing depends on the frequency of vibration.
- collet
collet
Flexible-sided device that secures a tool or workpiece. Similar in function to a chuck, but can accommodate only a narrow size range. Typically provides greater gripping force and precision than a chuck. See chuck.
- computer numerical control ( CNC)
computer numerical control ( CNC)
Microprocessor-based controller dedicated to a machine tool that permits the creation or modification of parts. Programmed numerical control activates the machine’s servos and spindle drives and controls the various machining operations. See DNC, direct numerical control; NC, numerical control.
- countersink
countersink
Tool that cuts a sloped depression at the top of a hole to permit a screw head or other object to rest flush with the surface of the workpiece.
- dish
dish
Form of relief given to the face of an endmill to prevent undesirable contact with the work. Similar to clearance.
- endmill
endmill
Milling cutter held by its shank that cuts on its periphery and, if so configured, on its free end. Takes a variety of shapes (single- and double-end, roughing, ballnose and cup-end) and sizes (stub, medium, long and extra-long). Also comes with differing numbers of flutes.
- flat ( screw flat)
flat ( screw flat)
Flat surface machined into the shank of a cutting tool for enhanced holding of the tool.
- flutes
flutes
Grooves and spaces in the body of a tool that permit chip removal from, and cutting-fluid application to, the point of cut.
- fluting
fluting
Cutting straight or spiral grooves in drills, endmills, reamers and taps to improve cutting action and remove chips.
- grinding
grinding
Machining operation in which material is removed from the workpiece by a powered abrasive wheel, stone, belt, paste, sheet, compound, slurry, etc. Takes various forms: surface grinding (creates flat and/or squared surfaces); cylindrical grinding (for external cylindrical and tapered shapes, fillets, undercuts, etc.); centerless grinding; chamfering; thread and form grinding; tool and cutter grinding; offhand grinding; lapping and polishing (grinding with extremely fine grits to create ultrasmooth surfaces); honing; and disc grinding.
- land
land
Part of the tool body that remains after the flutes are cut.
- outer diameter ( OD)
outer diameter ( OD)
Dimension that defines the exterior diameter of a cylindrical or round part. See ID, inner diameter.
- pitch
pitch
1. On a saw blade, the number of teeth per inch. 2. In threading, the number of threads per inch.
- polycrystalline diamond ( PCD)
polycrystalline diamond ( PCD)
Cutting tool material consisting of natural or synthetic diamond crystals bonded together under high pressure at elevated temperatures. PCD is available as a tip brazed to a carbide insert carrier. Used for machining nonferrous alloys and nonmetallic materials at high cutting speeds.
- relief
relief
Space provided behind the cutting edges to prevent rubbing. Sometimes called primary relief. Secondary relief provides additional space behind primary relief. Relief on end teeth is axial relief; relief on side teeth is peripheral relief.
- shank
shank
Main body of a tool; the portion of a drill or similar end-held tool that fits into a collet, chuck or similar mounting device.

