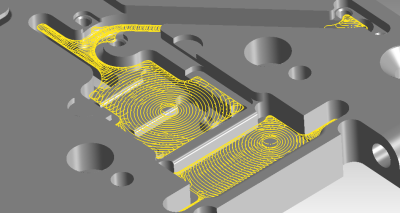
SmartCAMcnc has announced the release of SmartCAM v2019. The SmartCAM CAM software family consists of applications for CNC milling, turning, fabrication and wire EDM.
SmartCAM v2019 delivers new adaptive solid-pocket and solid-planar processes in the SmartCAM Advanced Milling, Advanced Turning and Freeform Machining applications, providing consistent-engagement high-speed milling toolpath for roughing solid or surface models. Also included are many customer-requested changes to the SmartCAM user interface and core functionality. Additionally, a variety of improvements to NC code generation provide added flexibility.
"Following the well-received integration of Adaptive Roughing technology to our wireframe processes in v2018, we're excited to be continuing that with our solids processes in v2019. Our Advanced Milling and Turning and FreeForm users will now be able to quickly and easily create high speed adaptive milling toolpath directly from a solid," said Doug Oliver, senior product manager at SmartCAMcnc.
The new adaptive solid pocket process is used to create consistent-engagement high speed rough milling toolpath when pocketing on solid or surface models.
The CAD solid model may contain a single or multiple closed pocket features, and can be comprised of any number of islands and "shelves." Pocket walls can be vertical or drafted and bottom fillet radii are supported by the process.
A new adaptive solid planar roughing process has also been added to the adaptive milling toolpath modeling task set.
The process is used to create consistent-engagement high speed rough milling toolpath when it is required to remove material from a stock volume on solid or surface-models. The model may consist of any combination of core and cavity features, with open or closed, blind or through regions, and can include any number of islands and shelves. The process is suitable for roughing simple prismatic parts through to complex-surface molds and dies.
"We have had many users provide positive feedback on their experiences using the adaptive processes, and we anticipate they will find the solid pocket and planar adaptive processes even more productive," Oliver said.
SmartCAM v2019 benefits from detail changes that deliver to SmartCAM applications a further refined and refreshed appearance, as well as improved ease of use.
- Individually Sized Toolbars – the size of individual toolbars is easily set by right-clicking on it and using the fly-out menu to select a large, medium or small setting for that toolbar.
- Optional Text on Toolbars – An option has been introduced to allow the display of text around the icon used on toolbar buttons.
- Toolbar Sets – A toolbar set stores the toolbars that are enabled in the user interface, where they are located on-screen, their orientation, the icon size for each toolbar, and whether button text is displayed and where it is positioned as per the user's preferences.
- Zoom View to Active Group – The ability to zoom the graphics view to the extent of the selected "active" group has been added.
- Gradient background in the graphics window.
Improvements to NC Code Generation Include:
- Handling of Hole-Milling operations – The result of multiple customer requests, a new code generator section is called to handle milled hole (as opposed to drilled) machining operations, the code generator calls this new section when a hole feature element is being machined with a nonhole operation type.
- Code Generator/Macro System Integration – The ability to set decimal, integer and string macro variables during code generation has been added.
- Setting Decimal, Integer and String Macro Variables during Code Generation – has been added and allows for reading of the macro string variables within the code generation mechanism.
- Wrapped Geometry Handling improvements - provide both higher quality toolpath and better handling of it by the code generator.
Core Improvements Include:
- New 64-bit SmartCAM applications - SmartCAM v2019 NC applications are now available in both 32-bit and 64-bit versions. The 64-bit version makes better use of modern computer hardware, allowing it to run applications quicker and address more RAM memory.
- Knowledge-Based Machining Enhancements - Improved associativity for the knowledge base manager
- Verification - View Section – When SmartCAM Verification is paused, view section parameters can be used to change the view section settings and the updated settings will be immediately applied.
- Wire EDM Upper/Lower Guide Offsets – The SmartCAM Advanced Wire EDM roughing- and finishing-operations now include new wire guide offset inputs. The upper guide offset specifies the distance from the toolpath Prof Top to the wire top above. The lower guide offset specifies the distance from the toolpath Level to the wire bottom below. These settings are used by Verify when displaying wire electrodes.
- Updated solid modeling kernel - SmartCAM v2019 includes the most-current ACIS 2018 SP2 solid modeling kernel.
- Updated data translators - SmartCAM v2019 includes updated CAD data translators for SOLIDWORKS data files.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- computer numerical control ( CNC)
computer numerical control ( CNC)
Microprocessor-based controller dedicated to a machine tool that permits the creation or modification of parts. Programmed numerical control activates the machine’s servos and spindle drives and controls the various machining operations. See DNC, direct numerical control; NC, numerical control.
- computer-aided design ( CAD)
computer-aided design ( CAD)
Product-design functions performed with the help of computers and special software.
- computer-aided manufacturing ( CAM)
computer-aided manufacturing ( CAM)
Use of computers to control machining and manufacturing processes.
- electrical-discharge machining ( EDM)
electrical-discharge machining ( EDM)
Process that vaporizes conductive materials by controlled application of pulsed electrical current that flows between a workpiece and electrode (tool) in a dielectric fluid. Permits machining shapes to tight accuracies without the internal stresses conventional machining often generates. Useful in diemaking.
- fillet
fillet
Rounded corner or arc that blends together two intersecting curves or lines. In three dimensions, a fillet surface is a transition surface that blends together two surfaces.
- gang cutting ( milling)
gang cutting ( milling)
Machining with several cutters mounted on a single arbor, generally for simultaneous cutting.
- milling
milling
Machining operation in which metal or other material is removed by applying power to a rotating cutter. In vertical milling, the cutting tool is mounted vertically on the spindle. In horizontal milling, the cutting tool is mounted horizontally, either directly on the spindle or on an arbor. Horizontal milling is further broken down into conventional milling, where the cutter rotates opposite the direction of feed, or “up” into the workpiece; and climb milling, where the cutter rotates in the direction of feed, or “down” into the workpiece. Milling operations include plane or surface milling, endmilling, facemilling, angle milling, form milling and profiling.
- numerical control ( NC)
numerical control ( NC)
Any controlled equipment that allows an operator to program its movement by entering a series of coded numbers and symbols. See CNC, computer numerical control; DNC, direct numerical control.
- solid model
solid model
3-D model created using “building blocks.” This is the most accurate way of representing real-world objects in CAD.
- toolpath( cutter path)
toolpath( cutter path)
2-D or 3-D path generated by program code or a CAM system and followed by tool when machining a part.
- turning
turning
Workpiece is held in a chuck, mounted on a face plate or secured between centers and rotated while a cutting tool, normally a single-point tool, is fed into it along its periphery or across its end or face. Takes the form of straight turning (cutting along the periphery of the workpiece); taper turning (creating a taper); step turning (turning different-size diameters on the same work); chamfering (beveling an edge or shoulder); facing (cutting on an end); turning threads (usually external but can be internal); roughing (high-volume metal removal); and finishing (final light cuts). Performed on lathes, turning centers, chucking machines, automatic screw machines and similar machines.
- wire EDM
wire EDM
Process similar to ram electrical-discharge machining except a small-diameter copper or brass wire is used as a traveling electrode. Usually used in conjunction with a CNC and only works when a part is to be cut completely through. A common analogy is wire electrical-discharge machining is like an ultraprecise, electrical, contour-sawing operation.
