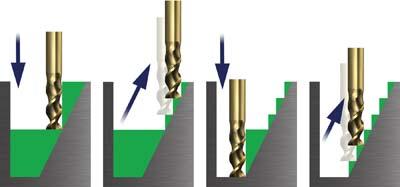
CNC Software Inc.'s OptiRough is a new technique designed to remove large amounts of material quickly using its successful dynamic milling motion. Large, aggressive cuts are followed by fast, smaller up-cuts, safely delivering a fully roughed part faster than ever. Mastercam's new 3D surface high speed OptiRough toolpath supports cutters capable of machining very large depths of cut.
A single OptiRough toolpath can cut material in two directions: on step-downs (-Z) and step-ups (+Z). This highly efficient, bi-directional cutting strategy removes the maximum amount of material with the minimum of step-downs, significantly reducing cycle times.
"The beauty of OptiRough is that you don't need any special tooling to use it. It simply uses the tools you have now, but in a much more efficient way," says Gary Hargreaves, VP, Business Development.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- computer numerical control ( CNC)
computer numerical control ( CNC)
Microprocessor-based controller dedicated to a machine tool that permits the creation or modification of parts. Programmed numerical control activates the machine’s servos and spindle drives and controls the various machining operations. See DNC, direct numerical control; NC, numerical control.
- gang cutting ( milling)
gang cutting ( milling)
Machining with several cutters mounted on a single arbor, generally for simultaneous cutting.
- milling
milling
Machining operation in which metal or other material is removed by applying power to a rotating cutter. In vertical milling, the cutting tool is mounted vertically on the spindle. In horizontal milling, the cutting tool is mounted horizontally, either directly on the spindle or on an arbor. Horizontal milling is further broken down into conventional milling, where the cutter rotates opposite the direction of feed, or “up” into the workpiece; and climb milling, where the cutter rotates in the direction of feed, or “down” into the workpiece. Milling operations include plane or surface milling, endmilling, facemilling, angle milling, form milling and profiling.
- toolpath( cutter path)
toolpath( cutter path)
2-D or 3-D path generated by program code or a CAM system and followed by tool when machining a part.
