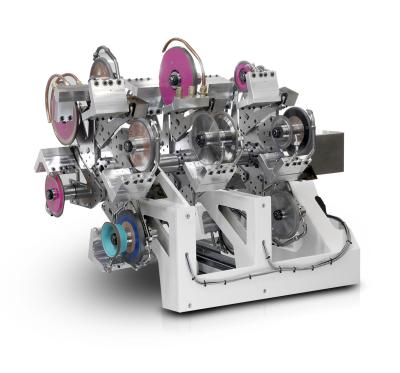
Rollomatic, a leading machine tool manufacturer based in Le Landeron, Switzerland, maintains its global leadership position in the field of 6-axis CNC tool grinding by highlighting the model 630XW3 with a 16-station wheel changer. This model is part of the GrindSmart® series of tool & cutter grinding machines with an axis configuration that incorporates 6 fully interpolated axes (3 rotary and 3 linear) and is unique in this industry. The machine also incorporates linear axis drive technology.
GrindSmart® 6-axis tool grinding machine with 16-station wheel and nozzle changer.
Highlights:
- Simultaneous change of wheel packs and associated coolant manifolds with coolant nozzles.
- World’s smallest footprint of a 16-station wheel changer (only ads 30” to the width of the machine).
- Tool unload/load happens simultaneously during wheel change to shorten cycle time.
- Embedded intelligence to keep frequently used wheel packs in front to shorten cycle time.
- The wheel arbors are HSK-type with a proprietary attachment design that guarantees less than .00005” TIR over the life of the grinding spindle.
- Allows highest productivity in small-batch grinding of complex and high-performance cutting tools.
- Enhanced autonomy.
- Uses Rollomatic’s VGPro desk top tool design program.
- Machines are assembled under a lean manufacturing program.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- computer numerical control ( CNC)
computer numerical control ( CNC)
Microprocessor-based controller dedicated to a machine tool that permits the creation or modification of parts. Programmed numerical control activates the machine’s servos and spindle drives and controls the various machining operations. See DNC, direct numerical control; NC, numerical control.
- coolant
coolant
Fluid that reduces temperature buildup at the tool/workpiece interface during machining. Normally takes the form of a liquid such as soluble or chemical mixtures (semisynthetic, synthetic) but can be pressurized air or other gas. Because of water’s ability to absorb great quantities of heat, it is widely used as a coolant and vehicle for various cutting compounds, with the water-to-compound ratio varying with the machining task. See cutting fluid; semisynthetic cutting fluid; soluble-oil cutting fluid; synthetic cutting fluid.
- grinding
grinding
Machining operation in which material is removed from the workpiece by a powered abrasive wheel, stone, belt, paste, sheet, compound, slurry, etc. Takes various forms: surface grinding (creates flat and/or squared surfaces); cylindrical grinding (for external cylindrical and tapered shapes, fillets, undercuts, etc.); centerless grinding; chamfering; thread and form grinding; tool and cutter grinding; offhand grinding; lapping and polishing (grinding with extremely fine grits to create ultrasmooth surfaces); honing; and disc grinding.
- grinding machine
grinding machine
Powers a grinding wheel or other abrasive tool for the purpose of removing metal and finishing workpieces to close tolerances. Provides smooth, square, parallel and accurate workpiece surfaces. When ultrasmooth surfaces and finishes on the order of microns are required, lapping and honing machines (precision grinders that run abrasives with extremely fine, uniform grits) are used. In its “finishing” role, the grinder is perhaps the most widely used machine tool. Various styles are available: bench and pedestal grinders for sharpening lathe bits and drills; surface grinders for producing square, parallel, smooth and accurate parts; cylindrical and centerless grinders; center-hole grinders; form grinders; facemill and endmill grinders; gear-cutting grinders; jig grinders; abrasive belt (backstand, swing-frame, belt-roll) grinders; tool and cutter grinders for sharpening and resharpening cutting tools; carbide grinders; hand-held die grinders; and abrasive cutoff saws.
- lean manufacturing
lean manufacturing
Companywide culture of continuous improvement, waste reduction and minimal inventory as practiced by individuals in every aspect of the business.
- total indicator runout ( TIR)
total indicator runout ( TIR)
Combined variations of all dimensions of a workpiece, measured with an indicator, determined by rotating the part 360°.

