ESPRIT-To-VERICUT Interface
ESPRIT-To-VERICUT Interface
CGTech and DP Technology are pleased to announce the availability of the ESPRIT-to-VERICUT Interface. The interface launches VERICUT NC verification, machine simulation and optimization software from within ESPRIT 2012 CAM software.
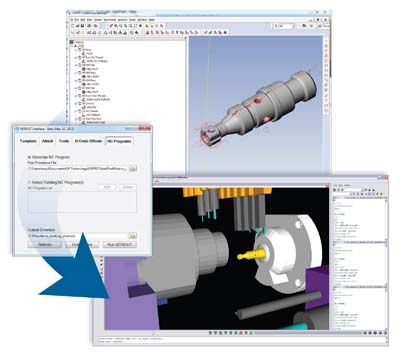
CGTech and DP Technology are pleased to announce the availability of the ESPRIT-to-VERICUT Interface. The interface launches VERICUT NC verification, machine simulation and optimization software from within ESPRIT 2012 CAM software.
"Accurately simulating the CNC machine and material removal with the actual NC code that will run on the machine is a requirement for the complex CNC machines and machining processes supported by ESPRIT users," said CGTech's Product Marketing Manager Bill Hasenjaeger. "Working together, the ESPRIT/VERICUT combination provides a comprehensive solution to help prevent errors from being forwarded to the shop floor — avoiding material scrap, machine damage, broken tools and wasted time."
"We are pleased to partner with CGTech and provide our customers with a link to VERICUT from ESPRIT, which provides easy access to VERICUT NC verification and machine-simulation software," said David Bartholomew, technical marketing specialist for DP Technology, maker of ESPRIT CAM.
The ESPRIT-to-VERICUT Interface tightly integrates the two programs to help users create the most accurate and efficient NC programs possible. The tools, fixtures and stock material created in ESPRIT are seamlessly transferred into VERICUT, which is automatically set up in the correct orientation and coordinate system to allow simulation to start immediately. Both the kinematics and CNC control of each machine tool are accurately modeled and defined inside VERICUT, ensuring the checks mirror the exact behavior of the CNC machine.
By simulating CNC programs on a computer without using the actual machine tool, ESPRIT users are able to realize significant savings and efficiencies by reducing machine cycle time, improving work quality and maximizing throughput. Possible programming errors are identified sooner without putting the actual machine tool at risk.





