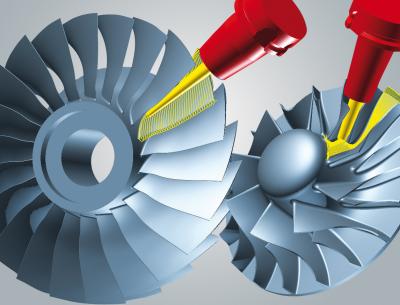
SoftInWay Inc. and OPEN MIND Technologies AG announce a cooperation agreement to provide a complete solution for the design, development and manufacturing of gas turbine components and other types of turbomachinery. Both companies reportedly provide component developers the needed productivity tools to accelerate the product development and production process while maintaining a high level of accuracy.
The AxSTREAM Software Platform provides an integrated and streamlined approach to turbomachinery design. The software consists of a number of different modules to perform preliminary design, meanline and streamline analysis, CFD and FEA, blade profiling, and rotor dynamics, bearings analysis, and rotor design for compressors, pumps and turbines. These tools are used to produce optimal components, considering speed, power, range and life. The interactive and user-friendly design process enables these conditions to be achieved efficiently and reliably.
hyperMILL is a modular complete CAM solution for 2.5D, 3D, 5-axis, HSC/HPC, and mill-turning processes as well as its special applications and highly efficient automation solutions. The CAM software provides technology-leading geometry analysis and tool path calculations. There are specialized routines designed for efficient programming and machining of these components on 5-axis milling or mill-turn machines. The multi-blade and single-blade turbomachinery solutions are embedded within hyperMILL that is applied to more broad-based milling, drilling and turning applications, allowing an all-in-one CAM system for turbomachinery developers. Robust CNC postprocessors are also provided to assure strong communication to machine tool controllers.
This partnership between SoftInWay and OPEN MIND brings product, services, sales and technical teams together for a complete software solution. Customers can work with each company to obtain tools, training and services from these companies. Both companies are well represented with direct employees and authorized resellers in America, Europe and Asia and look forward to collaborating together to contribute towards the advancement of the turbomachinery industry.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- computer numerical control ( CNC)
computer numerical control ( CNC)
Microprocessor-based controller dedicated to a machine tool that permits the creation or modification of parts. Programmed numerical control activates the machine’s servos and spindle drives and controls the various machining operations. See DNC, direct numerical control; NC, numerical control.
- computer-aided manufacturing ( CAM)
computer-aided manufacturing ( CAM)
Use of computers to control machining and manufacturing processes.
- gang cutting ( milling)
gang cutting ( milling)
Machining with several cutters mounted on a single arbor, generally for simultaneous cutting.
- milling
milling
Machining operation in which metal or other material is removed by applying power to a rotating cutter. In vertical milling, the cutting tool is mounted vertically on the spindle. In horizontal milling, the cutting tool is mounted horizontally, either directly on the spindle or on an arbor. Horizontal milling is further broken down into conventional milling, where the cutter rotates opposite the direction of feed, or “up” into the workpiece; and climb milling, where the cutter rotates in the direction of feed, or “down” into the workpiece. Milling operations include plane or surface milling, endmilling, facemilling, angle milling, form milling and profiling.
- profiling
profiling
Machining vertical edges of workpieces having irregular contours; normally performed with an endmill in a vertical spindle on a milling machine or with a profiler, following a pattern. See mill, milling machine.
- turning
turning
Workpiece is held in a chuck, mounted on a face plate or secured between centers and rotated while a cutting tool, normally a single-point tool, is fed into it along its periphery or across its end or face. Takes the form of straight turning (cutting along the periphery of the workpiece); taper turning (creating a taper); step turning (turning different-size diameters on the same work); chamfering (beveling an edge or shoulder); facing (cutting on an end); turning threads (usually external but can be internal); roughing (high-volume metal removal); and finishing (final light cuts). Performed on lathes, turning centers, chucking machines, automatic screw machines and similar machines.

