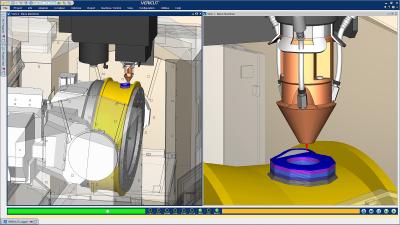
CGTech has introduced additive manufacturing enhancements to be released in VERICUT version 9.0. VERICUT CNC machine simulation, verification and optimization software simulates all types of CNC machining, additive and hybrid manufacturing processes. The software operates independently, but can also be integrated with leading CAM systems.
“With VERICUT, NC programmers and planners are able to determine which additive equipment and build strategies will work best,” said CGTech Product Manager Gene Granata. “By simulating real NC data on digital twin machines, VERICUT can prevent expensive crashes, identify conflicting setups and ensure additive functions are properly controlled by the NC program.”
VERICUT 9.0 includes several advancements for additive manufacturing. Users can add material and cut via any traditional machining operation, in any desired order. Version 9’s enhanced graphics provide sharper views of the additive processes, and flexibility to rotate or zoom while simulating. Users can verify the entire manufacturing process and ensure additively manufactured parts match engineered designs, by simulating all machining setups including post-process finishing. Analysis tools include the ability to section and measure additive parts, report on build times and volumes of material used.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- computer numerical control ( CNC)
computer numerical control ( CNC)
Microprocessor-based controller dedicated to a machine tool that permits the creation or modification of parts. Programmed numerical control activates the machine’s servos and spindle drives and controls the various machining operations. See DNC, direct numerical control; NC, numerical control.
- computer-aided manufacturing ( CAM)
computer-aided manufacturing ( CAM)
Use of computers to control machining and manufacturing processes.
- numerical control ( NC)
numerical control ( NC)
Any controlled equipment that allows an operator to program its movement by entering a series of coded numbers and symbols. See CNC, computer numerical control; DNC, direct numerical control.
