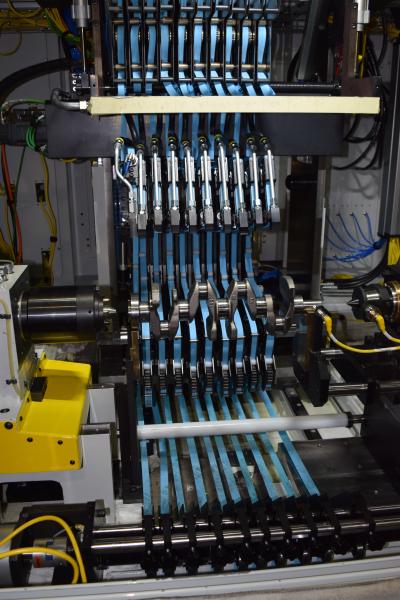
A new design CNC microfinishing system by IMPCO Microfinishing polishes the critical cylindrical bearing journals of a range of different size crankshafts to micron tolerances consistently and automatically without the need to manually change and reposition the tooling, reducing changeover time from many hours to a few minutes. The company says its Worldstar 1680 is a fully flexible microfinishing system for the automotive industry and was built in response to the requirements of a European automaker for installation in Brazil.
Microfinishing is the process that removes the microscopic amorphous surface material left from the grinding of a dimensionally finished part, such as a crankshaft, camshaft or pump shaft, to permit a highly precise fit to a mating part. IMPCO microfinishing is used to generate the final functional surface texture required for friction reduction, higher performance and greater reliability of the precision shafts. Microfinishing tolerances are unattainable with grinding.
“In today’s automotive engines, the surface texture on these functional key features on the internal engine components are microfinished to very fine tolerances that enable combustion engines to operate more efficiently and to meet emissions, horsepower and fuel economy goals,” said Mark Hendel, IMPCO global sales director.
In the IMPCO microfinishing machine, abrasive film is fed through a pair of opposed arms, each holding tooling that is shaped to fit over the part’s cylindrical bearing journals. During the process, the arms close around the journals, holding the film against the rotating part for a specified time to achieve the desired surface texture.
The part may undergo several increasingly fine levels of finishing to produce the final finish. The IMPCO machine processes a 4-cylinder crankshaft through three levels of microfinishing plus thrust face finishing. In the automotive industry, surface finish parameters used to evaluate the surfaces of the crankshafts include Ra, Rk, Rpk and Rvk.
The flexibility of the machine to automatically position any of its 11 pairs of arms in any position to accommodate a range of crankshaft sizes will save the automaker time during changeover and avoid the need to retool the machine. The machine will permit the automaker to produce any crankshaft in its matrix of part dimensions, including variation on bearing pitch (main bearing to pin bearing spacing), currently and into the future.
Each microfinishing station in the four-machine system is loaded and unloaded automatically with an overhead gantry.
According to the company, it has been pursuing development of this machine for more than a year in response to a global need for flexibility to produce parts to a range of specifications and volumes with minimum changeover time and cost.
“Our global customer demanded the machine capability and our staff and plant here in Lansing delivered the solution,” said Pat Cebelak, IMPCO president and CEO.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- abrasive
abrasive
Substance used for grinding, honing, lapping, superfinishing and polishing. Examples include garnet, emery, corundum, silicon carbide, cubic boron nitride and diamond in various grit sizes.
- amorphous
amorphous
Not having a crystal structure; noncrystalline.
- computer numerical control ( CNC)
computer numerical control ( CNC)
Microprocessor-based controller dedicated to a machine tool that permits the creation or modification of parts. Programmed numerical control activates the machine’s servos and spindle drives and controls the various machining operations. See DNC, direct numerical control; NC, numerical control.
- grinding
grinding
Machining operation in which material is removed from the workpiece by a powered abrasive wheel, stone, belt, paste, sheet, compound, slurry, etc. Takes various forms: surface grinding (creates flat and/or squared surfaces); cylindrical grinding (for external cylindrical and tapered shapes, fillets, undercuts, etc.); centerless grinding; chamfering; thread and form grinding; tool and cutter grinding; offhand grinding; lapping and polishing (grinding with extremely fine grits to create ultrasmooth surfaces); honing; and disc grinding.
- micron
micron
Measure of length that is equal to one-millionth of a meter.
- pitch
pitch
1. On a saw blade, the number of teeth per inch. 2. In threading, the number of threads per inch.
- surface texture
surface texture
Repetitive or random deviations from the nominal surface, which form 3-D topography of the surface. See flows; lay; roughness; waviness.
