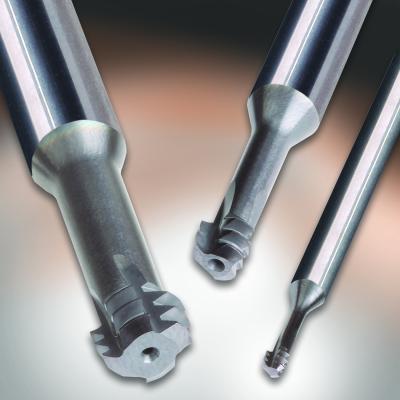
Emuge Corp. has introduced advanced Threads-all ZGF-S-Cut solid-carbide thread mills featuring multiple teeth, a helical flute form and multiple-layer TiAlN T46 coating. The new ZGF-S-Cut thread mills increase tool life over 10 times more than conventional tools and produce precise threads in exotic materials including Inconels, nickel-based superalloys, monel, titanium, 420 stainless steel and more.
"To efficiently thread challenging, expensive materials we are very pleased to offer our new ZGF-S-Cut Thread Mills," said Marlon Blandon, thread milling product manager, Emuge Corp. "The new thread mills are an ideal solution when threading Inconel and other high temperature alloys because the heat is carried away during chip evacuation and does not stay with the part. The new tools are excellent for producing finer threads in aerospace applications such as engines, connecting rods and landing gear, as well as in other components comprised of exotic materials."
For increased tool life and productivity, Emuge ZGF-S-Cut thread mills have multiple teeth, the first acting as a rougher and the next two teeth performing finishing. By dividing functions into three cutting edges, speeds and feeds can be increased, and threads can be produced in a single pass. A 10° left-hand helical flute form and chamfer geometry combine to optimize chip evacuation in the forward direction and add strength to the cutting teeth for enhanced tool life and process security. And for increased tool strength, Emuge ZGF-S-Cut Thread Mills have multiple flutes.
The tools are available in 2xD lengths, have coolant-fed options starting at 1/4" diameter, and one tool easily makes STI threads for both through- and blind-holes. ZGF-S-Cut thread mills are offered in inch sizes ranging from No.2 or M3 through 7/16 or M10.
The entire Emuge Threads-all ZGF program of premium sub-micrograin carbide thread mills encompasses solutions for the production of internal threads from No. 0-80 (M1) to 3/4-16. for demanding industries using difficult materials such as stainless steel, titanium and Inconel. Coolant fed options are available starting at the 5/16" diameter size. Available in 2xD and 3xD lengths in both miniature and standard thread sizes, the Threads-all family of thread mills provides high quality, dependable solutions for the toughest applications with full bottoming threading within 1 pitch. Threads-all tools provide total control over pitch diameter limits including 2B, 3B, 3BG and all oversize variants. Single plane and multiple plane tools are offered.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- alloys
alloys
Substances having metallic properties and being composed of two or more chemical elements of which at least one is a metal.
- coolant
coolant
Fluid that reduces temperature buildup at the tool/workpiece interface during machining. Normally takes the form of a liquid such as soluble or chemical mixtures (semisynthetic, synthetic) but can be pressurized air or other gas. Because of water’s ability to absorb great quantities of heat, it is widely used as a coolant and vehicle for various cutting compounds, with the water-to-compound ratio varying with the machining task. See cutting fluid; semisynthetic cutting fluid; soluble-oil cutting fluid; synthetic cutting fluid.
- flutes
flutes
Grooves and spaces in the body of a tool that permit chip removal from, and cutting-fluid application to, the point of cut.
- gang cutting ( milling)
gang cutting ( milling)
Machining with several cutters mounted on a single arbor, generally for simultaneous cutting.
- milling
milling
Machining operation in which metal or other material is removed by applying power to a rotating cutter. In vertical milling, the cutting tool is mounted vertically on the spindle. In horizontal milling, the cutting tool is mounted horizontally, either directly on the spindle or on an arbor. Horizontal milling is further broken down into conventional milling, where the cutter rotates opposite the direction of feed, or “up” into the workpiece; and climb milling, where the cutter rotates in the direction of feed, or “down” into the workpiece. Milling operations include plane or surface milling, endmilling, facemilling, angle milling, form milling and profiling.
- pitch
pitch
1. On a saw blade, the number of teeth per inch. 2. In threading, the number of threads per inch.
- superalloys
superalloys
Tough, difficult-to-machine alloys; includes Hastelloy, Inconel and Monel. Many are nickel-base metals.
- threading
threading
Process of both external (e.g., thread milling) and internal (e.g., tapping, thread milling) cutting, turning and rolling of threads into particular material. Standardized specifications are available to determine the desired results of the threading process. Numerous thread-series designations are written for specific applications. Threading often is performed on a lathe. Specifications such as thread height are critical in determining the strength of the threads. The material used is taken into consideration in determining the expected results of any particular application for that threaded piece. In external threading, a calculated depth is required as well as a particular angle to the cut. To perform internal threading, the exact diameter to bore the hole is critical before threading. The threads are distinguished from one another by the amount of tolerance and/or allowance that is specified. See turning.
- titanium aluminum nitride ( TiAlN)
titanium aluminum nitride ( TiAlN)
Often used as a tool coating. AlTiN indicates the aluminum content is greater than the titanium. See coated tools.

