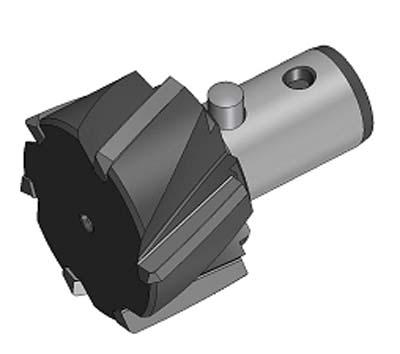
Seco Tools Inc. has announced the development of grade RX2000 with a surface hardness coating of up to 3,200 HV for increased productivity and tool life in Seco Precimaster reaming system applications, which feature exchangeable throwaway heads. The new RX coating has a low friction co-efficient to minimize the risk of built-up edge and improve chip evacuation. In conjunction with a micrograin substrate, this super-thin (0.00008") coating provides enhanced surface finish, chip control and tool life, according to the company. When compared to other reaming grades, the RX2000 has reportedly shown a 200 percent increase in tool life in forged steel applications. The RX2000 is well-suited for all materials except nonferrous, and works well in mass production application environments that can handle increased cutting data. The Precimaster reaming system combines a well-engineered body with internal through-coolant capability for through- or blind-hole finishing. Exchangeable reaming heads are available in sizes from 4mm to 60mm. The clamping system allows for accurate repositioning of the cutting head for H7 hole tolerance achievement. Additionally, the location of the clamp on the tool body makes it easy to change reaming heads without removing the tool from the machining spindle.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- Vickers hardness number ( HV)
Vickers hardness number ( HV)
Number related to the applied load and surface area of the permanent impression made by a square-based pyramidal diamond indenter having included face angles of 136º. The Vickers hardness number is a ratio of the applied load in kgf, multiplied by 1.8544, and divided by the length of diagonal squared.
- blind-hole
blind-hole
Hole or cavity cut in a solid shape that does not connect with other holes or exit through the workpiece.
- built-up edge ( BUE)
built-up edge ( BUE)
1. Permanently damaging a metal by heating to cause either incipient melting or intergranular oxidation. 2. In grinding, getting the workpiece hot enough to cause discoloration or to change the microstructure by tempering or hardening.
- hardness
hardness
Hardness is a measure of the resistance of a material to surface indentation or abrasion. There is no absolute scale for hardness. In order to express hardness quantitatively, each type of test has its own scale, which defines hardness. Indentation hardness obtained through static methods is measured by Brinell, Rockwell, Vickers and Knoop tests. Hardness without indentation is measured by a dynamic method, known as the Scleroscope test.
- tolerance
tolerance
Minimum and maximum amount a workpiece dimension is allowed to vary from a set standard and still be acceptable.