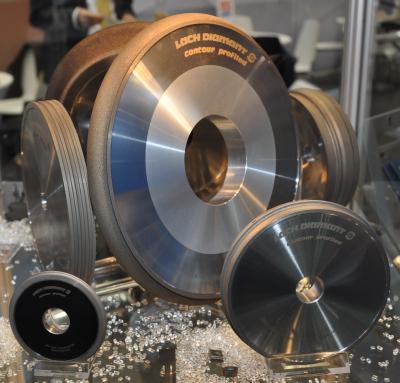
Metal-bond profiled diamond and CBN grinding wheels are available for serial grinding of workpieces made of carbides, hardened steels and ceramics. Lach Diamond says its »contour-profiled« procedure is a cost killer in the best possible way. Previous grinding times with resin/hybrid-bond grinding wheels can be reduced by up to 60 percent.
During deep grinding of threading inserts, the profiled grinding wheels reduce two to three work steps to one single process. The company developed this production procedure, which allows for the manufacturing of almost any profile – concave or convex – at the smallest possible tolerances of up to 0.005 mm.
In addition, metal-bond grinding wheels from Lach Diamond maximize tool life, by far exceeding previous resin bonds.
In regards to maintenance – i.e. reprofiling and regrinding of Lach diamond and CBN grinding wheels – Lach Diamond guarantees 100 percent renewal or reproduction of the original profile and degree of precision and not only once, but multiple times.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- ceramics
ceramics
Cutting tool materials based on aluminum oxide and silicon nitride. Ceramic tools can withstand higher cutting speeds than cemented carbide tools when machining hardened steels, cast irons and high-temperature alloys.
- cubic boron nitride ( CBN)
cubic boron nitride ( CBN)
Crystal manufactured from boron nitride under high pressure and temperature. Used to cut hard-to-machine ferrous and nickel-base materials up to 70 HRC. Second hardest material after diamond. See superabrasive tools.
- grinding
grinding
Machining operation in which material is removed from the workpiece by a powered abrasive wheel, stone, belt, paste, sheet, compound, slurry, etc. Takes various forms: surface grinding (creates flat and/or squared surfaces); cylindrical grinding (for external cylindrical and tapered shapes, fillets, undercuts, etc.); centerless grinding; chamfering; thread and form grinding; tool and cutter grinding; offhand grinding; lapping and polishing (grinding with extremely fine grits to create ultrasmooth surfaces); honing; and disc grinding.
- threading
threading
Process of both external (e.g., thread milling) and internal (e.g., tapping, thread milling) cutting, turning and rolling of threads into particular material. Standardized specifications are available to determine the desired results of the threading process. Numerous thread-series designations are written for specific applications. Threading often is performed on a lathe. Specifications such as thread height are critical in determining the strength of the threads. The material used is taken into consideration in determining the expected results of any particular application for that threaded piece. In external threading, a calculated depth is required as well as a particular angle to the cut. To perform internal threading, the exact diameter to bore the hole is critical before threading. The threads are distinguished from one another by the amount of tolerance and/or allowance that is specified. See turning.
