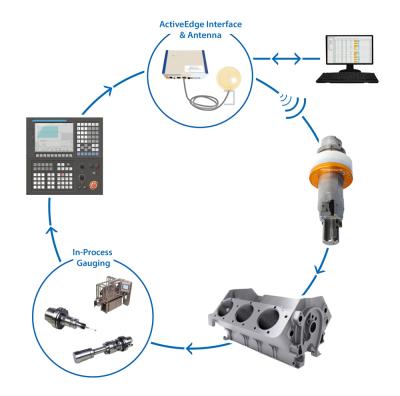
Zenith is Rigibore’s automated solution to producing micron accurate bores. The Zenith solution offers significant savings and a tangible return on investment by reducing labor costs, eliminating scrap and supporting 24-hour production through lights-out manufacturing.
CNC machines, regardless of their sophistication, cannot automatically compensate a boring tool's cutting edges. Rigibore's ActiveEdge tooling, in combination with in-process bore measurement, has overcome this problem.
The Zenith system integrates ActiveEdge tools with in-process gauging to enable a machine controller to automatically compensate for insert wear, temperature changes and material inconsistency without manual intervention and without stopping the manufacturing process.
Rigibore refers to this process as closed-loop tool compensation, eliminating scrap and enabling organizations to meet precise tolerances and production targets in a consistent and repeatable manner.
This automated, closed-loop boring cycle provides a number of short term and long term production benefits:
- Industry 4.0 Ready.
- Reduced Cycle Time - Optimized Manufacturing Process.
- Improved Process Control - Automatic Adjustment For Wear Compensation.
- Lights-Out Manufacturing - 24-Hour Production Capabilities.
- Maximised Spindle Utilization - Cutting Edge Adjustment Anywhere in the Machine.
- Return On Investment - Removed Operator Intervention and Eliminated Risk of Scrap.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- boring
boring
Enlarging a hole that already has been drilled or cored. Generally, it is an operation of truing the previously drilled hole with a single-point, lathe-type tool. Boring is essentially internal turning, in that usually a single-point cutting tool forms the internal shape. Some tools are available with two cutting edges to balance cutting forces.
- computer numerical control ( CNC)
computer numerical control ( CNC)
Microprocessor-based controller dedicated to a machine tool that permits the creation or modification of parts. Programmed numerical control activates the machine’s servos and spindle drives and controls the various machining operations. See DNC, direct numerical control; NC, numerical control.
- micron
micron
Measure of length that is equal to one-millionth of a meter.
- process control
process control
Method of monitoring a process. Relates to electronic hardware and instrumentation used in automated process control. See in-process gaging, inspection; SPC, statistical process control.

