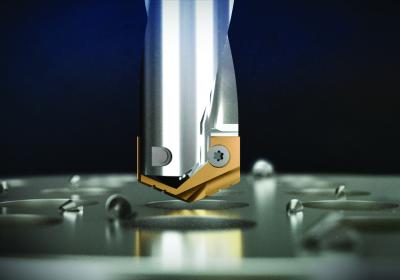
YG-1 SV-Point spade drill inserts provide longer tool life at higher spindle speeds and feeds than conventional spade drills.
SV-Point spade drill inserts offer exceptional performance in a wide range of applications and materials including steel, stainless steel and cast iron.
- H-Coating for high heat and wear resistance
- Sinusoidal thinning edge for smooth cutting and improved centering
- Positive rake angle for improved hole finish
- Low thrust force – excellent option for underpowered machines
Three material options:
- Super Cobalt (T15) — For improved tool life and performance over standard HSS inserts – size range: 9.5mm to 114.3mm
- Premium Cobalt (M48) — Extended tool life over T15 in harder materials – size range: 9.5mm to 114.3mm
- Carbide C5 (P40) — For longer tool life and faster speeds & feeds in rigid setups – size range: 9.5mm to 47.6mm
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- centering
centering
1. Process of locating the center of a workpiece to be mounted on centers. 2. Process of mounting the workpiece concentric to the machine spindle. See centers.
- high-speed steels ( HSS)
high-speed steels ( HSS)
Available in two major types: tungsten high-speed steels (designated by letter T having tungsten as the principal alloying element) and molybdenum high-speed steels (designated by letter M having molybdenum as the principal alloying element). The type T high-speed steels containing cobalt have higher wear resistance and greater red (hot) hardness, withstanding cutting temperature up to 1,100º F (590º C). The type T steels are used to fabricate metalcutting tools (milling cutters, drills, reamers and taps), woodworking tools, various types of punches and dies, ball and roller bearings. The type M steels are used for cutting tools and various types of dies.
- rake
rake
Angle of inclination between the face of the cutting tool and the workpiece. If the face of the tool lies in a plane through the axis of the workpiece, the tool is said to have a neutral, or zero, rake. If the inclination of the tool face makes the cutting edge more acute than when the rake angle is zero, the rake is positive. If the inclination of the tool face makes the cutting edge less acute or more blunt than when the rake angle is zero, the rake is negative.
- spade drill
spade drill
Flat end-cutting tool used to produce holes ranging from about 1" to 6" in diameter. Spade drills consist of an interchangeable cutting blade and a toolholder that has a slot into which the blade fits. In horizontal applications, universal spade drills can achieve extreme depth-to-diameter ratios, but, in vertical applications, the tools are limited by poor chip evacuation.
- wear resistance
wear resistance
Ability of the tool to withstand stresses that cause it to wear during cutting; an attribute linked to alloy composition, base material, thermal conditions, type of tooling and operation and other variables.

