Capto Toolholders and Larger Insert Widths for Grooving
Capto Toolholders and Larger Insert Widths for Grooving
Walter has added Walter Capto toolholders and insert widths to its Walter Cut MX grooving system. Capto toolholders feature enhanced rigidity and modularity, while the tapered polygonal shape handles both torsional and bending forces with ease. This interface can be used for lathes and turn/mill centers.
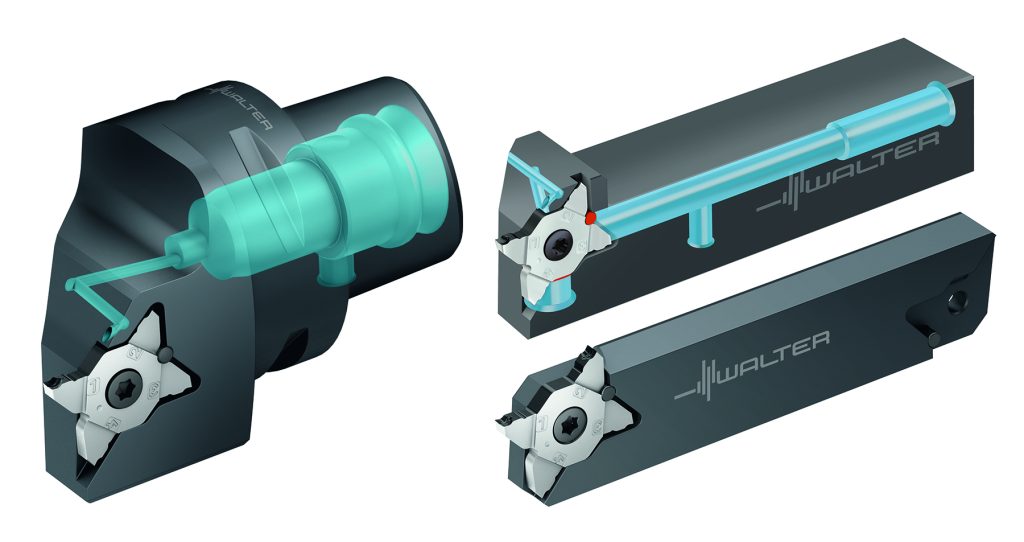
Walter has added Walter Capto toolholders and insert widths to its Walter Cut MX grooving system. Capto toolholders feature enhanced rigidity and modularity, while the tapered polygonal shape handles both torsional and bending forces with ease. This interface can be used for lathes and turn/mill centers.
With the new Walter Capto monoblock tools (C3–C6), the MX system can now also be used on machines with Capto interfaces. In addition, new parting blades are introduced to work with automatic lathes and multiple-spindle machines. Walter has completed the range with new grooving inserts and toolholders for larger insert widths. Where previously only 0.031 in. (0.80 mm) to a maximum of 0.128 in. (3.25 mm) were possible, the insert width now ranges up to 0.222 in. (5.65 mm)—including the very common dimensions of 0.125 in. (3.18. 0.157 in (4 mm) and 0.196 (5 mm). Maximum cutting depth is 0.24 in. (6 mm).
These extensions are intended to make new applications possible for users of the MX grooving system, from small-parts production where a high degree of precision is needed; to job shops, where the focus is on fast, precise tool changes and cost efficiency.
The Walter Cut MX grooving system uses dowel pin location to prevent improper assembly of inserts into the holders. The dowel pin location along with the horizontal seating surface also provides high positioning accuracy and diameter repeatability for the inserts; thus, eliminating the need for "test cuts" after every cutting edge of insert change. With a unique design, the four-edge indexable inserts can be used even after one or more cutting edge breaks for maximum cost efficiency. The inserts also have a very long tool life thanks to the Walter-specific precision cooling and the Tiger·tec Silver grades.






