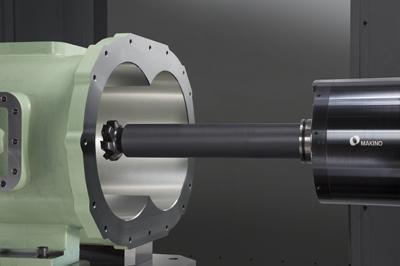
Makino announced the new a81nx horizontal machining center. Like Makino&'s other nx-Series horizontal machining centers, the a51nx and a61nx, the a81nx extends the capabilities of its 1-series predecessor with expanded machining capacity, improved rigidity and stability, improved productivity and enhanced reliability, according to the company.
"The a81nx builds on the success of the original a81 platform and sets a new standard for large-part machining performance," said Dave Ward, horizontal product line manager at Makino. "There have been enhancements made to the bed and column castings of the machine, expansions in the tool magazine and Y-axis travels, spindle design improvements for faster acceleration and deceleration times, and a host of additional features and advancements to improve ergonomics, maintenance and machine uptime."
When it comes to large-part machining, a limited work zone can hinder even the most efficient cutting processes and technologies. This is the reason why the a81nx features a 100-mm extension of the Y-axis column, bringing full-axis travels along the X, Y and Z axes to 35.4 inches, 35.4 inches and 40.2 inches (900mm, 900mm and 1,020mm), respectively. The increased Y-axis travel is especially beneficial for automotive parts such as engine blocks and cylinder heads, where the critical mating surfaces require feed-on/feed-off milling passes for optimal sealing.
Large parts also commonly contain a substantial volume of features that can range greatly in size, requiring quick accessibility to diverse tool types and sizes. The a81nx provides a robust automatic tool changer (ATC) that is designed to handle larger-diameter, longer and heavier tooling. This large tool capacity ensures that manufacturers are able to efficiently machine a variety of large part features.
For improved speed and productivity, the a81nx is standardly equipped with a 10,000-rpm spindle that affords 305 Nm of duty-rated torque and 45kW of extended-duty power (26 kW of continuous output). Duty-rated power levels have increased 25 percent over the previous model. Such an enhancement dramatically reduces spindle acceleration and deceleration times, saving 20 to 30 percent in tapping processes.
An optional 8,000-rpm, high-torque spindle configuration is also available for manufacturers working with hard metals. With 553 Nm of duty-rated torque and 37 kW of continuous output, this spindle option delivers 19 percent more continuous power output over the previous high-torque spindle, enabling manufacturers to take on more aggressive cutting conditions in ferrous and difficult-to-machine materials.
Other advanced productivity features of the a81nx include a new GI servo control mode that can reduce pocketing times for aluminum billet applications, and a new chain-type, 80-tool-capacity automatic tool-change magazine for reduced tool-seek times.
Makino's 1-series horizontal machining centers have a reputation for endurance and toughness. The nx-Series machines leverage this proven design to enhance rigidity and reliability with several new, advanced features.
The a81nx bed, column and table castings feature enhanced build qualities, including an increased step height between the front and rear X-axis linear guide for improved strength and higher acceleration. For greater stiffness and reliability in higher load capacities, the machine uses roller-type linear motion guides. The a81nx B-axis table is available in two configurations—index and NC rotary. Each configuration has been redesigned for improved rigidity, including a larger curvic coupling diameter within the index table and the use of a three-roller-type bearing in the NC rotary table for superior rigidity and thrust support.
With millions of tool changes occurring during the life of a machine, the reliability of the ATC is crucial. The nx-Series machines feature a high-speed servo-driven ball screw that actuates the ATC shutter door, improving responsiveness, ease of setup and maintenance. The servo axis also reduces exposure of the ATC to the work envelope. The additions of taper-cleaning air-blow station and tool-seat detection ensure that all tools are clean and properly seated in the spindle. The net result is improved reliability and cleaner ATC environments.
In order for machines to reach maximum efficiency, they must be designed to provide operators with a comfortable and user-friendly work environment. The ergonomically friendly, L-shaped door design of the a81nx offers operators greater accessibility to the spindle, enhanced visibility for inspection of the tool or part and coolant drip prevention at the doorway. Additionally, preventive maintenance features on the a81nx have been relocated to a concentrated area on the machine's back panels for easy access.
The safety-guard door on the automatic pallet changer (APC) has an adjustable height for the operation panel and can be moved to match the level of the operator's work platform. A wider APC stocker improves the loading of large fixtures and workpieces, and allows easy chip cleaning.
The addition of a tool-loading station on all magazines helps improve the ergonomics of handling large, heavy tools. A touch-type human machine interface panel is also available on all 80-tool capacity ATCs or larger, providing an easy way to manage tool data while at the ATC magazine.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- centers
centers
Cone-shaped pins that support a workpiece by one or two ends during machining. The centers fit into holes drilled in the workpiece ends. Centers that turn with the workpiece are called “live” centers; those that do not are called “dead” centers.
- coolant
coolant
Fluid that reduces temperature buildup at the tool/workpiece interface during machining. Normally takes the form of a liquid such as soluble or chemical mixtures (semisynthetic, synthetic) but can be pressurized air or other gas. Because of water’s ability to absorb great quantities of heat, it is widely used as a coolant and vehicle for various cutting compounds, with the water-to-compound ratio varying with the machining task. See cutting fluid; semisynthetic cutting fluid; soluble-oil cutting fluid; synthetic cutting fluid.
- gang cutting ( milling)
gang cutting ( milling)
Machining with several cutters mounted on a single arbor, generally for simultaneous cutting.
- machining center
machining center
CNC machine tool capable of drilling, reaming, tapping, milling and boring. Normally comes with an automatic toolchanger. See automatic toolchanger.
- milling
milling
Machining operation in which metal or other material is removed by applying power to a rotating cutter. In vertical milling, the cutting tool is mounted vertically on the spindle. In horizontal milling, the cutting tool is mounted horizontally, either directly on the spindle or on an arbor. Horizontal milling is further broken down into conventional milling, where the cutter rotates opposite the direction of feed, or “up” into the workpiece; and climb milling, where the cutter rotates in the direction of feed, or “down” into the workpiece. Milling operations include plane or surface milling, endmilling, facemilling, angle milling, form milling and profiling.
- numerical control ( NC)
numerical control ( NC)
Any controlled equipment that allows an operator to program its movement by entering a series of coded numbers and symbols. See CNC, computer numerical control; DNC, direct numerical control.
- stiffness
stiffness
1. Ability of a material or part to resist elastic deflection. 2. The rate of stress with respect to strain; the greater the stress required to produce a given strain, the stiffer the material is said to be. See dynamic stiffness; static stiffness.
- tapping
tapping
Machining operation in which a tap, with teeth on its periphery, cuts internal threads in a predrilled hole having a smaller diameter than the tap diameter. Threads are formed by a combined rotary and axial-relative motion between tap and workpiece. See tap.
- work envelope
work envelope
Cube, sphere, cylinder or other physical space within which the cutting tool is capable of reaching.

