Industrial robotic applications have been growing exponentially across multiple industrial ecosystems, as value-addition to the existing operational paradigms become imperative. Rising eminence of collaborative robots (cobots) in the future is not surprising as automation continues to lie at the heart of industrial spaces for both regular and complex applications. Cost is also a key factor responsible for the rise of industrial robotics, owing to the fact that the average selling prices of robots have come down significantly over the past 20 to 30 years.
Manufacturers of robotic components are reaping benefits out of the sheer proliferation of automation and industrial robotics alike. One of such high-in-demand category of robotic components is the robotic EOAT (end-of-arm tooling), which refers to composite systems of grippers used for handling delicate or large components. Being an indispensable aspect of robotic technology, robotic EOAT is witnessing strong adoption, owing to their significance in equipping the robots with specific functionalities.
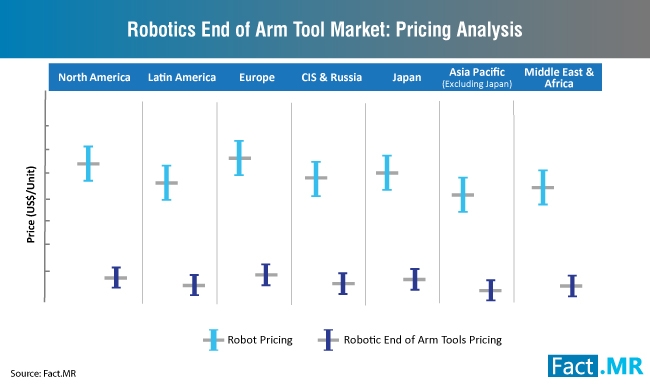
What Does the Future Hold for Robotic EOAT Sales?
Global sales of robotic EOAT witnessed impressive growth at a CAGR of over 8% from 2013 to 2017. Further gains are anticipated to grow at a CAGR of over 10% through 2028, by virtue of the fact that industrial robotic installations worldwide are growing by leaps and bounds. With majority of the industries vying to stay at the forefront of Industry 4.0, the installed base of robotic systems worldwide has become higher than ever, fuelling investments in the robotic EOAT market.
Grippers are estimated to sell more than other types of robotic EOAT, as pick-and-place applications remain a staple of the automation framework. Selection of the gripper type, such as magnetic grippers, jaw grippers, niddle grippers, and bellows grippers, is determined by nature of the concerned end-use application. This can be gauged from the fact that global demand for grippers was valued at over US$ 1,000 Mn in 2018, up from over US$ 940 Mn in 2017.
Opportunities Abound as Industrial Robotics Installation Continues on the Upswing
There is no denying that when it comes to technological advancements, the robotic EOAT landscape is undergoing a sea change. Impeccable deployment of robots and faultless fixation of accessories will gain higher importance than robots alone. Apart from just being used for handling weight and shape variations, the use of EOAT is also gaining prominence for the accommodation of multiple processes simultaneously. This, in turn, is estimated to offer bountiful opportunities for the companies operating in the robotic EOAT market. Industrial operators are willing to spend more on effective and agile EOAT to achieve production targets via unmatched flexibility and speed, thereby boosting profitability of manufacturers in the future.
EOAT offers faster and better return of investment for manufacturers on account of their flexibility and easy deployment, making EOAT fall into the list of viable investments taken into account by industrial operators. Moreover, robotic EOAT enables industry operators to switch uninterruptedly between multiple tasks with minimal requirements of tool swapping or additional programming, thereby setting industry operators free from the switching costs. Such particulars shed light on the unabated demand for robotic EOAT in the future, creating revenue-generating opportunities for the manufacturers.
While robotic EOAT manufacturers continue to raise their game in creating tools of basic formats (primarily vacuum, magnet or mechanical), they are also focusing on developing custom EOAT, including the ones meant for handling specific materials. SCHUNK GmbH & Co. KG, a leading German-based manufacturer, is popular for its custom-made grippers. While some interesting growth patterns are emerging across the developed countries with respect to demand for robotic EOAT, developing economies, such as China, will see unprecedented rise in demand owing to automation surge. Adoption of EOAT will also see robust growth in India for many years to come, as the regional industrial paradigms are undergoing a drastic makeover.
Automotive is likely to have the largest base of robotic installments followed by electronics. Both automotive and electronic industries are relying on robots for effortless handling of the complex manufacturing systems. Hence, the industrial operators of automotive and electronics seek exceptional flexibility of robots to carry out multitasking and, subsequently, invest in effective EOAT to achieve the same. With electronics and automotive sectors leading the race of automation, they are highly likely to account for industry-specific demand for robotic EOAT.
When it comes to making purchase decisions, price is generally not of primary importance for majority of the industries buying robotic EOAT. This is true especially in case of industries such as automotive wherein the interruption costs, if the production lines are down, become exceptionally high. However, reliability continues to be a key decisive factor for industrial operators to make purchases in the robotic EOAT space.
High Manufacturing Costs Pose Consequential Challenges for Manufacturers
Robotic EOAT entails maintenance on a timely basis for ensuring smooth and undisturbed operations, thereby arresting its adoption and posing challenges for the growth of robotic EOAT market. Lack of meticulous maintenance on a regular basis leads to unwanted impacts on the robotic end-of-arm tools, hampering their overall productivity and effectiveness.
In addition, high costs of developing and manufacturing robotic EOAT is another restraining factor, as higher production costs have adverse impact on the final product prices. High production costs result in high sales prices of final products, thereby causing significant losses for the key stakeholders in the market. Skepticism among some industrial operators with respect to robotic systems is also estimated to create unfavorable circumstances for the robotic EOAT manufacturers.
The future of robotic EOAT market looks promising as industrial units continue to rely on robots that operate with precision of the highest standard. With the fast-paced acceleration of this trend, robotic EOAT manufacturers will be able to capture most of the profit pools. However, it cannot be denied that major technological breakthroughs in the robotics space could possibly disrupt the robotic EOAT industry and lead to major changes in the supply-demand parameters. It remains to be seen how the industry stakeholders will catch up with these disruptions and make the most out of it for long-term profitability.
For more information, click here.
Related Glossary Terms
- robotics
robotics
Discipline involving self-actuating and self-operating devices. Robots frequently imitate human capabilities, including the ability to manipulate physical objects while evaluating and reacting appropriately to various stimuli. See industrial robot; robot.

