Article from API
Cole Technologies Inc., Columbus, Indiana, is a certified Universal Robots system integrator that supplies automation systems specializing in pick-and-place, deburring and plastic part trimming applications. One recent project involved the deflashing of molded parts where a more accurate robot path was deemed necessary.
Cole Technologies contracted API Services to perform on-site robot calibration using the API Radian 6DoF (6 degrees of freedom) laser tracker, in conjunction with its proprietary Robot Measuring Software (RMS), to improve programmed robot motion path accuracy.
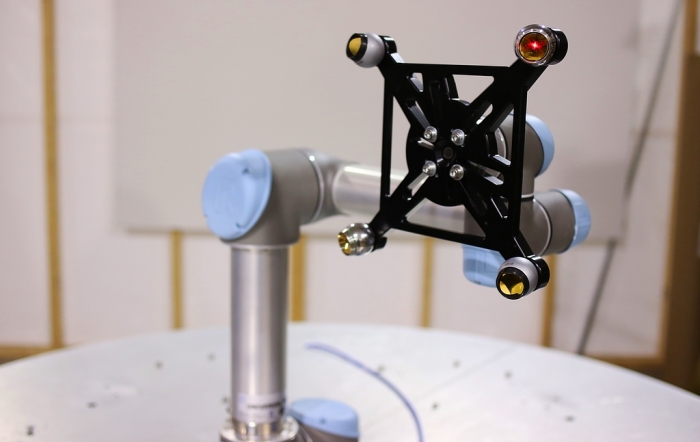
The multi-SMR robot calibration frame.
The RMS system uses a multiple SMR tracker target frame directly mounted onto the robot end effector, allowing for dynamic robot tracking. Recorded measurements are used to determine tracked robot position points revealing true robot position and orientation. RMS procedures use ISO-9283 guidelines to check accuracy, repeatability, pose, distance, drift and overshoot by exercising all robot joints. Robot working envelope can be defined applicable to the planned robot application function.
“The availability of additional robot accuracy allows us to provide a better outcome for the customer regardless of application,” stated Steve Richard, director of engineering at Cole Technologies. “API were able to directly interface with our RoboDK robot programming software for robot calibration, making it seamless and efficient to load the new parameters.”
![]()
The API Radian 6DoF laser tracker performs robot calibration.
Measuring a free point cloud consisting of 80 points, the RMS software generated a new DH (Denavit-Hartenberg) frame model parameter set that was used to correct errors in joint angles and link lengths. The revised DH parameter can be directly input into the robot controller or used to update the robot motion path program as was the case at Cole Technologies, resulting in significant improvements to robot accuracy.
To view an application video, visit https://youtu.be/F86fKA782rE.
Related Glossary Terms
- calibration
calibration
Checking measuring instruments and devices against a master set to ensure that, over time, they have remained dimensionally stable and nominally accurate.
- overshoot
overshoot
Deviation from nominal path caused by momentum carried over from previous step, as when a tool is rapidly traversed a considerable distance to begin a cut. Usually applies to CNC machining and is prevented if the control has the appropriate look-ahead capability. See look-ahead; undershoot.
