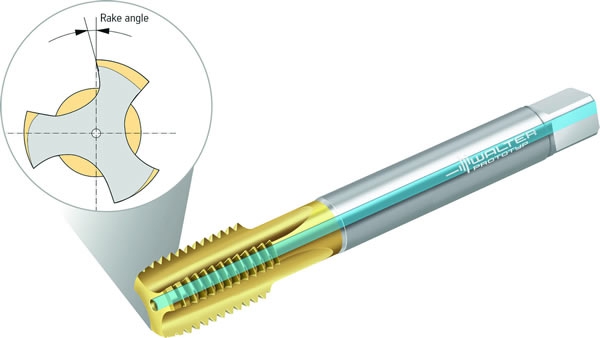
 Walter has expanded its popular Paradur HT HSS-E blind-hole tap range by adding UNC thread dimensions. Previously available in dimensions M4-M36 and M10×1-M33×2, Walter has now expanded the range of the taps to include dimensions UNC 1/4-UNC 1. These new HSS-E taps are particularly well suited to cutting deep threads of up to 3.5 × DN. Like their predecessors, they include performance enhancing features such as straight flutes, axial through coolant, and a TiN coating.
Walter has expanded its popular Paradur HT HSS-E blind-hole tap range by adding UNC thread dimensions. Previously available in dimensions M4-M36 and M10×1-M33×2, Walter has now expanded the range of the taps to include dimensions UNC 1/4-UNC 1. These new HSS-E taps are particularly well suited to cutting deep threads of up to 3.5 × DN. Like their predecessors, they include performance enhancing features such as straight flutes, axial through coolant, and a TiN coating.
The specially designed cutting-edge geometry of the Paradur HT tap range affords excellent chip control. Axial through coolant reliably flushes short chips out of blind-holes. Ideal for machining steel with tensile strength of 98-200 kpsi (200-410 HB) and for cast iron, especially for GJS (GGG). The new tools offer a number of benefits for the user.
For one thing, "birdnesting" of chips is no longer an issue, which translates to high process reliability. Enhanced tool life significantly reduces machine downtime which is perfect for production environments using minimal manpower. Paradur HT taps are also cost-effective, while at the same time performance enhancing. These taps are typically used in the energy and in general metalworking industries.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- blind-hole
blind-hole
Hole or cavity cut in a solid shape that does not connect with other holes or exit through the workpiece.
- coolant
coolant
Fluid that reduces temperature buildup at the tool/workpiece interface during machining. Normally takes the form of a liquid such as soluble or chemical mixtures (semisynthetic, synthetic) but can be pressurized air or other gas. Because of water’s ability to absorb great quantities of heat, it is widely used as a coolant and vehicle for various cutting compounds, with the water-to-compound ratio varying with the machining task. See cutting fluid; semisynthetic cutting fluid; soluble-oil cutting fluid; synthetic cutting fluid.
- flutes
flutes
Grooves and spaces in the body of a tool that permit chip removal from, and cutting-fluid application to, the point of cut.
- metalworking
metalworking
Any manufacturing process in which metal is processed or machined such that the workpiece is given a new shape. Broadly defined, the term includes processes such as design and layout, heat-treating, material handling and inspection.
- tap
tap
Cylindrical tool that cuts internal threads and has flutes to remove chips and carry tapping fluid to the point of cut. Normally used on a drill press or tapping machine but also may be operated manually. See tapping.
- tensile strength
tensile strength
In tensile testing, the ratio of maximum load to original cross-sectional area. Also called ultimate strength. Compare with yield strength.
- titanium nitride ( TiN)
titanium nitride ( TiN)
Added to titanium-carbide tooling to permit machining of hard metals at high speeds. Also used as a tool coating. See coated tools.

