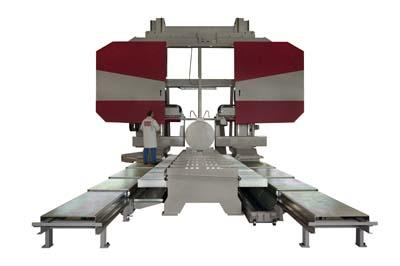
The new generation of large-scale saws from Behringer benefit from a consistently modular design principle and are available in three different models and four sizes. They are designed to allow users from different fields such as forging, steel manufacture, rolling mills, mould making or the steel trade to machine heavy and bulky materials quickly and precisely. They are able to guarantee tolerances of just 0.1mm over a 100mm cutting height. By maximizing the number of identical parts used across the series, production and assembly are speeded up, ensuring shorter delivery periods. This standardization of components in the new large-scale saw series opens up enormous scope for individual customization. The wide vertical range of production practised by the Baden-Württemberg-based manufacturer guarantees top-quality workmanship, structural stability, reliability and a long service life. Particularly when it comes to large-scale bandsaws, which are generally required to operate around the clock in three shifts, these are precisely the attributes that count. Thanks to an in-house foundry, Behringer GmbH supplies just about everything it needs for its own production from the molten iron to the finished machine.
From a cutting range of over two metres, the large bandsaws feature four band running wheels and a precise saw feed system using two ball screws with servo drive. Electrically coupled axes guarantee constant chip removal even at low feed rates. The result: A perfect and precise cut every time.
A gantry machine in which the entire saw frame is moved on linear guides over the workpiece is both the technically most complex solution, and the one requiring the least space. The sturdy fixed support table is capable of withstanding enormous loads of up to 100 tons. Adjustable prism supports allow simple workpiece alignment.
The table version presents the most suitable option primarily for applications involving the division of freeform forgings or large solid forged parts. A table variant permits high-precision material positioning in the sawing area. Benefiting from a highly sturdy design, this option is ideally suited for application in tough, hostile industrial environments, as the hard-wearing tables are capable of withstanding extreme loads and their guides are insensitive to dirt. Flexible lengths can also be configured using tables with variable traversing paths. Large-scale bandsaws with roller conveyor are ideally suited for dividing large pipes, round or flat material and are used predominantly in the steel trade.
The new generation of large bandsaws is available in four sizes:
2,100mm cutting range
1,800mm cutting range
1,300mm cutting range
1,100mm cutting range
An interesting design feature of the table and roller conveyor machines is a gantry-type machine frame providing the guarantee of optimum stability during sawing. It ensures the smooth running of saw bands, prevents distortion and reduces vibrations during the sawing process. All the band guiding elements are made of vibration-damping grey cast iron. This not only ensures less stress on the saw bands but also improves cutting precision. The open design makes for better access to the machine to change the saw band or for maintenance work. Two ball screws ensure constant movement even with low feed rates, and prevent skewing of the saw frame. By ensuring a more even load on the saw band, service life can be increased by some 20 per cent. Cutting feed is powered by two servo drive systems, making a major contribution to high cutting performance. The frequency-controlled 15kW drive system provides sufficient power for even the toughest of blocks. A large-scale transmission at the drive shaft and hollow shaft bearing make for one hundred per cent reliability. A combination of roller and hydraulically pretensioned carbide slideways ensures precise tool guidance and helps to dampen vibrations at the point where they are created. The guide arm adjusts automatically, and a carefully conceived chip discharge concept ensures that created chips are transported through the machine bed over a wide channel.
Generously dimensioned chip bins and a high-level ejection point reduce the need for frequent changing of chip bins. To permit improved belt cleaning during the sawing process, double brushes with an automatic adjustment feature are mounted on each side of the saw band. The high level of process reliability achieved by these machines allows low-manned machining operation over periods of several hours.
There is plenty that can be done to improve safety for operating staff and to make for better alignment before cutting by taking the necessary steps when locating multi-ton workpieces. The currently used method of using wooden wedges as a material support has proven successful with slabs and blocks. For round material, prism supports are the most effective option, as they ensure precise, central alignment of the material prior to cutting, can be firmly fixed on the table and also permit adjustment without the need for tools.
A possible option available for the gantry models is a clamping fixture for automatic cutting of rollers. This entails clamping the workpiece prior to sawing on adjustable prisms. The planned cuts are then programmed, simulated at the machine to prevent costly errors from the outset, and then the program is run through automatically. After cutting, the fixture prevents uncontrolled tilting of the separated material and so enhances operator safety. This facility permits low-manned processing of a complete day's production and substantially reduces downtimes.
A special laying flat fixture provides a valuable material handling aid for the table-top models. Heavy offcuts are engaged and laid flat in a controlled process after cutting. This enhances operator safety and offers a significant handling benefit during transport out of the machine. If the offcuts are required to remain in the vertical position, a receiving basket fixed on the table prevents uncontrolled tilting of the multi-ton parts and simplifies their safe outward transport.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- bandsaw blade ( band)
bandsaw blade ( band)
Endless band, normally with serrated teeth, that serves as the cutting tool for cutoff or contour band machines.
- feed
feed
Rate of change of position of the tool as a whole, relative to the workpiece while cutting.
- fixture
fixture
Device, often made in-house, that holds a specific workpiece. See jig; modular fixturing.
- flat ( screw flat)
flat ( screw flat)
Flat surface machined into the shank of a cutting tool for enhanced holding of the tool.
- modular design ( modular construction)
modular design ( modular construction)
Manufacturing of a product in subassemblies that permits fast and simple replacement of defective assemblies and tailoring of the product for different purposes. See interchangeable parts.
- sawing
sawing
Machining operation in which a powered machine, usually equipped with a blade having milled or ground teeth, is used to part material (cutoff) or give it a new shape (contour bandsawing, band machining). Four basic types of sawing operations are: hacksawing (power or manual operation in which the blade moves back and forth through the work, cutting on one of the strokes); cold or circular sawing (a rotating, circular, toothed blade parts the material much as a workshop table saw or radial-arm saw cuts wood); bandsawing (a flexible, toothed blade rides on wheels under tension and is guided through the work); and abrasive sawing (abrasive points attached to a fiber or metal backing part stock, could be considered a grinding operation).
- sawing machine ( saw)
sawing machine ( saw)
Machine designed to use a serrated-tooth blade to cut metal or other material. Comes in a wide variety of styles but takes one of four basic forms: hacksaw (a simple, rugged machine that uses a reciprocating motion to part metal or other material); cold or circular saw (powers a circular blade that cuts structural materials); bandsaw (runs an endless band; the two basic types are cutoff and contour band machines, which cut intricate contours and shapes); and abrasive cutoff saw (similar in appearance to the cold saw, but uses an abrasive disc that rotates at high speeds rather than a blade with serrated teeth).
