FARO Introduces the Focus3D Laser Scanner
FARO Introduces the Focus3D Laser Scanner
FARO Technologies Inc. introduces the new FARO Laser Scanner Focus3D, a high-performance 3-D laser scanner for detailed measurement and documentation.
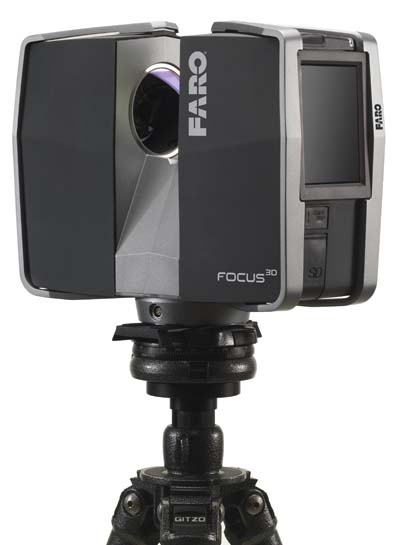

FARO Technologies Inc. introduces the new FARO Laser Scanner Focus3D, a high-performance 3-D laser scanner for detailed measurement and documentation with intuitive touch screen control that makes it as easy to operate as a digital camera. It is four times lighter and five times smaller than its predecessor.
Focus3D uses laser technology to produce detailed 3-D images of complex environments and geometries in only a few minutes. The resulting image is an assembly of millions of 3-D measurement points in color which provides an exact digital reproduction of existing conditions.
The new FARO Laser Scanner Focus3D is suitable for documentation of large environments, quality control of components and reverse engineering. The Focus3D is self-contained, meaning no additional devices, cables or laptop are needed. Its dimensions are 9.5 x 8 x 4" and it weighs 11lbs.
Focus3D deploys an integrated color camera with automatic and parallax free color overlay for photo-realistic 3-D scans. Its integrated lithium-ion high-performance battery provides up to five hours of battery life and can be charged during operation. All scans are stored on a SD card enabling easy and secure data transfer to a computer.
The FARO Focus3D is compatible with many common software applications. The flexible interfaces of SCENE, the scan processing software included with the Focus3D, enable connection to AutoCAD as well as many other CAD applications such as Rhino, Microstation, Nemetschek and ArchiCAD.