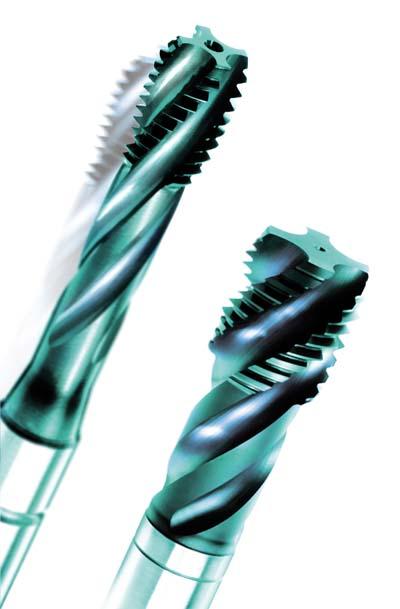
KOMET Group is expanding its portfolio of threading tools with the addition of the BASS line of high-speed steel machine taps and roll form taps. BASS threading tools provide high precision and reliable performance for all materials, and are offered in a wide range of sizes.
In partnership with BASS, KOMET has developed a stocking program in order to offer its customers a complement to its JEL brand of solid carbide and PCD threading and milling tools. Attractively priced, the BASS HSS-E and HSS-E powdered metal (PM) grade machine taps and roll form taps provide excellent performance for medium to low volume production in all industries.
"With our JEL product line, KOMET Group offers one of the most advanced solid carbide threading solutions in the industry, both for tapping as well as for thread milling," says Dr. F.- Hans Grandin, President/CEO, KOMET of America. "In 2012, we will focus on repeating the extraordinary success that KOMET Group experiences in the threading arena in other high-end international markets here in North America. Rounding off the JEL line with the BASS premium HSS taps is an integral element of this approach."
The BASS machine and roll form taps are designed to reduce the cost per thread, maximize the end-product quality and optimize the threading process.
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- gang cutting ( milling)
gang cutting ( milling)
Machining with several cutters mounted on a single arbor, generally for simultaneous cutting.
- high-speed steels ( HSS)
high-speed steels ( HSS)
Available in two major types: tungsten high-speed steels (designated by letter T having tungsten as the principal alloying element) and molybdenum high-speed steels (designated by letter M having molybdenum as the principal alloying element). The type T high-speed steels containing cobalt have higher wear resistance and greater red (hot) hardness, withstanding cutting temperature up to 1,100º F (590º C). The type T steels are used to fabricate metalcutting tools (milling cutters, drills, reamers and taps), woodworking tools, various types of punches and dies, ball and roller bearings. The type M steels are used for cutting tools and various types of dies.
- milling
milling
Machining operation in which metal or other material is removed by applying power to a rotating cutter. In vertical milling, the cutting tool is mounted vertically on the spindle. In horizontal milling, the cutting tool is mounted horizontally, either directly on the spindle or on an arbor. Horizontal milling is further broken down into conventional milling, where the cutter rotates opposite the direction of feed, or “up” into the workpiece; and climb milling, where the cutter rotates in the direction of feed, or “down” into the workpiece. Milling operations include plane or surface milling, endmilling, facemilling, angle milling, form milling and profiling.
- polycrystalline diamond ( PCD)
polycrystalline diamond ( PCD)
Cutting tool material consisting of natural or synthetic diamond crystals bonded together under high pressure at elevated temperatures. PCD is available as a tip brazed to a carbide insert carrier. Used for machining nonferrous alloys and nonmetallic materials at high cutting speeds.
- tapping
tapping
Machining operation in which a tap, with teeth on its periphery, cuts internal threads in a predrilled hole having a smaller diameter than the tap diameter. Threads are formed by a combined rotary and axial-relative motion between tap and workpiece. See tap.
- threading
threading
Process of both external (e.g., thread milling) and internal (e.g., tapping, thread milling) cutting, turning and rolling of threads into particular material. Standardized specifications are available to determine the desired results of the threading process. Numerous thread-series designations are written for specific applications. Threading often is performed on a lathe. Specifications such as thread height are critical in determining the strength of the threads. The material used is taken into consideration in determining the expected results of any particular application for that threaded piece. In external threading, a calculated depth is required as well as a particular angle to the cut. To perform internal threading, the exact diameter to bore the hole is critical before threading. The threads are distinguished from one another by the amount of tolerance and/or allowance that is specified. See turning.
