Emuge-Franken USA, Grob Systems Inc. and Open Mind Technologies are jointly holding a complimentary mold and die workshop July 20 from 10 a.m. to 1 p.m. ET at the Emuge Technology Center in West Boylston, Mass.
The workshop will cover via live machining demonstrations how to optimize mold and die accuracy by combining advanced tooling, machining, and CAM technologies.
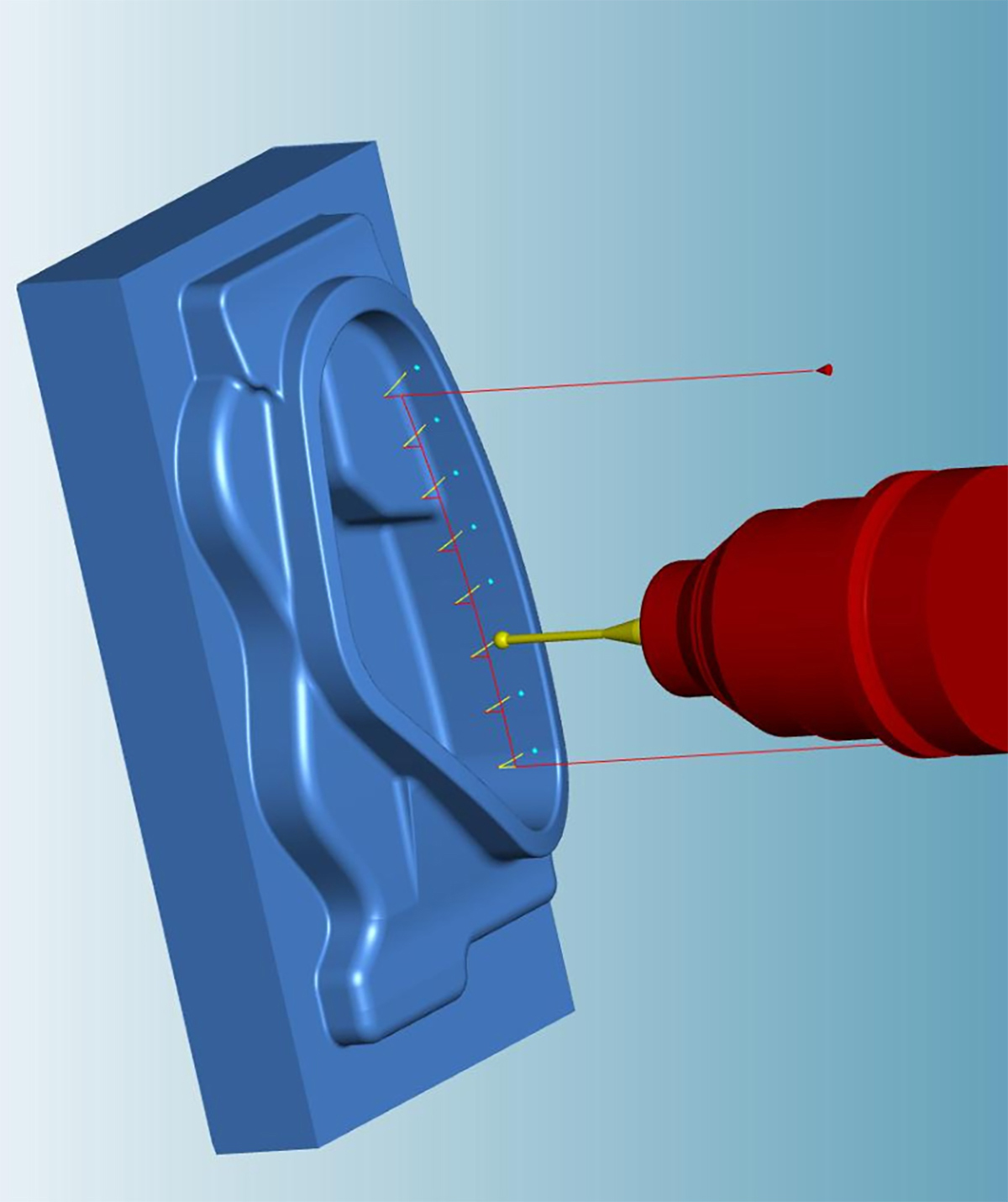
Attendees will learn how Open Mind’s hyperMILL CAM software machining strategies will maximize programming for Emuge-Franken tooling on a Grob G550a 5-axis CNC machining center.
To register for the event, go to https://info.emuge.com/enhancing-accuracy-in-mold-and-die-applications.
Key workshop topics and demonstrations will include:
--Achieving high-quality surface finishes with hyperMILL’s high precision surface mode by machining directly to the surface instead of an “approximated mesh,” and applying the CAM software’s smooth overlap capability which minimizes witness marks at the blending of adjoining part features.
--Utilizing the GROB G550a 5-Axis capabilities to properly orient and consistently maintain the Emuge-Franken Multi-Cut Duplex End Mill in the cut, while extending tool life.
--Maximizing the efficiency of the machining process with hyperMILL’s auto-indexing function to automatically generate multiple 3+2 segments as an alternative to 5-Axis.
--How to use shorter, smaller diameter tools for more aggressive machining by combining GROB’s rigid cross slide design and long Z-Axis stroke with hyperMILL’s 5-Axis rest machining strategy, and Emuge’s rigid FPC toolholder.
--Optimizing the workflow within multiple application stages by using process probing strategies.
Contact Details
Contact Details
Contact Details
Related Glossary Terms
- computer numerical control ( CNC)
computer numerical control ( CNC)
Microprocessor-based controller dedicated to a machine tool that permits the creation or modification of parts. Programmed numerical control activates the machine’s servos and spindle drives and controls the various machining operations. See DNC, direct numerical control; NC, numerical control.
- computer-aided manufacturing ( CAM)
computer-aided manufacturing ( CAM)
Use of computers to control machining and manufacturing processes.
- machining center
machining center
CNC machine tool capable of drilling, reaming, tapping, milling and boring. Normally comes with an automatic toolchanger. See automatic toolchanger.
- milling machine ( mill)
milling machine ( mill)
Runs endmills and arbor-mounted milling cutters. Features include a head with a spindle that drives the cutters; a column, knee and table that provide motion in the three Cartesian axes; and a base that supports the components and houses the cutting-fluid pump and reservoir. The work is mounted on the table and fed into the rotating cutter or endmill to accomplish the milling steps; vertical milling machines also feed endmills into the work by means of a spindle-mounted quill. Models range from small manual machines to big bed-type and duplex mills. All take one of three basic forms: vertical, horizontal or convertible horizontal/vertical. Vertical machines may be knee-type (the table is mounted on a knee that can be elevated) or bed-type (the table is securely supported and only moves horizontally). In general, horizontal machines are bigger and more powerful, while vertical machines are lighter but more versatile and easier to set up and operate.
- toolholder
toolholder
Secures a cutting tool during a machining operation. Basic types include block, cartridge, chuck, collet, fixed, modular, quick-change and rotating.


