Thread milling cutter with wear-resistant coating
Thread milling cutter with wear-resistant coating
The TD610 Supreme thread milling cutter family from Walter AG features highly wear-resistant HiPIMS coating WB10TU made of AlTiSiN. The company says the coating is extremely smooth, robust and wear-resistant, which that ensures a significantly longer service life compared to conventional coatings. In addition, the thread milling cutter has unique geometric features, such as the "trumpet bow neck," a tapered neck and groove geometry that reduces deflection, prevents tool breakage and allows regrinding in case of wear.
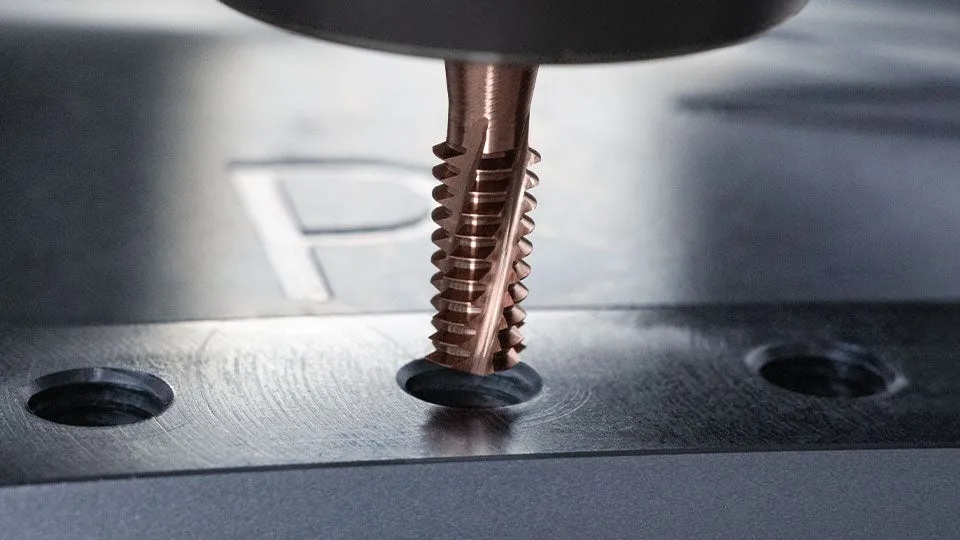

The TD610 Supreme thread milling cutter family from Walter AG features highly wear-resistant HiPIMS coating WB10TU made of AlTiSiN. The company says the coating is extremely smooth, robust and wear-resistant, which that ensures a significantly longer service life compared to conventional coatings. In addition, the thread milling cutter has unique geometric features, such as the "trumpet bow neck," a tapered neck and groove geometry that reduces deflection, prevents tool breakage and allows regrinding in case of wear.
The offset distribution of the flutes minimizes vibrations, especially with short threads, thereby improving thread quality and process reliability. This also applies to the special post-treatment of the TD610 Supreme, these polished cutting edges reduce wear, increase stability and improve thread quality even in the most demanding materials – while also increasing cutting speeds and reducing machining time. The full-profile thread milling cutter is universally applicable for blind and through threads in all ISO material groups, P, M, K, N and S, up to 48 HRC. Radius corrections are rare thanks to the stable process, which makes the TD610 Supreme ideal for both short-run or high-volume "lights-out" production. Walter offers the thread milling cutter for thread depths up to 1.5 × D(N), with and without internal cooling, and in many common standards like: M, MF, UNC, UNF and G. It should be of particular interest to users with demanding requirements, such as those working with expensive components.