ESAB launches next generation intuitive CNC controller
ESAB launches next generation intuitive CNC controller
ESAB has unveiled its Vision T6 CNC, a controller for automated plasma and oxy-fuel cutting machines that the company says is as intuitive to use as a smartphone or tablet. The Vision T6 features a multi-touch, high-definition panel with a Windows operating system. The Vision includes features such as swipe-to-zoom, drag-and-drop, and a familiar home button.
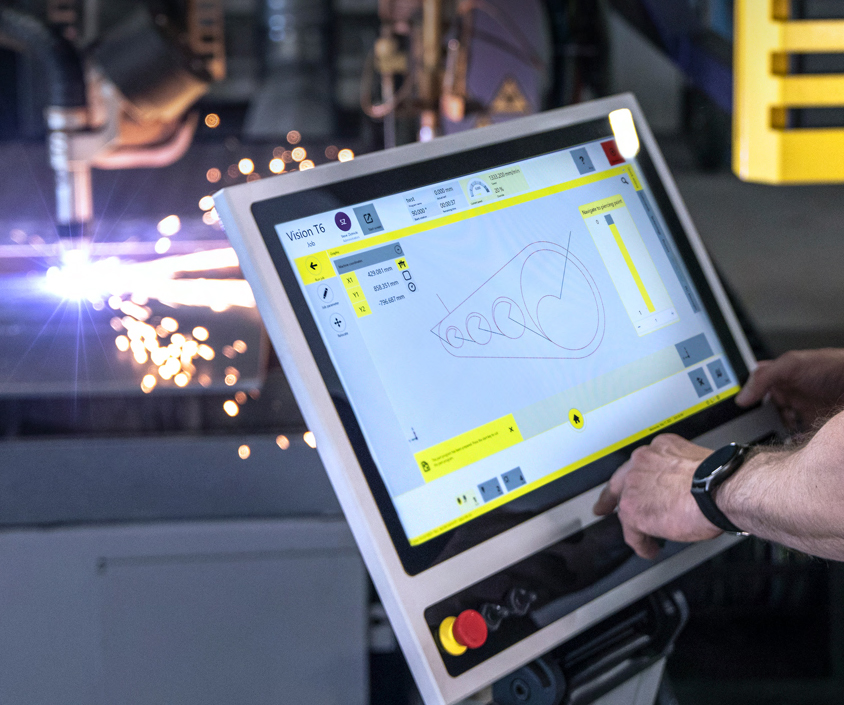
ESAB has unveiled its Vision T6 CNC, a controller for automated plasma and oxy-fuel cutting machines that the company says is as intuitive to use as a smart phone or tablet.
The Vision T6 features a multi-touch, high-definition panel with a Windows operating system. The Vision includes features such as swipe-to-zoom, drag-and-drop, and a familiar home button. The home button gives quick and easy access to a full range of features and capabilities, letting operators select and edit programs, create nests, locate parts on a plate, and cut, the company says.
The new Vision T6 has a 546 mm (21.5-in.) high-definition display that is 16% larger as compared to the Vision T5. The control housing is machined from a single aluminum billet for a sleek and rugged display. The Vision T6 is available for both new machines and retrofit applications, and supports ESAB's wide range of cutting, beveling, and marking tools, including the DMX Plasma Beveler. These machines are used by fabricators and manufacturers of all sizes, steel service centers, and defense contractors.
The Vision T6 connects with Columbus, which is ESAB's CAD/CAM programming and nesting software, now part of the InduSuite family of fabrication software products.
Users can choose the optional EasyNest feature for automatic, true-shape nesting right at the machine. The Vision T6 works seamlessly with the InduSuite CutCloud connected application to collect data from the Vision T6 to provide information and insights to improve productivity.
With the Vision T6's new plate and part awareness function, operators do not need to physically align the plate (e.g., physically square it with the table and measure its position). Instead, the operator can jog the machine to the plate corners or pick points along a plate remnant, even if it's an irregular shape. The controller then knows the exact shape, size and location of the plate on the table displayed graphically for operators to see. Operators can then choose a program and simply drag and drop the part or parts nest onto the plate and it will snap to the correct position. Operators do not have to worry about lining up the part; the Vision T6 controller does it for them, ensuring accuracy without the need for a dry run.
ESAB integrates all process controls into the Vision T6, simplifying operation and reducing manual errors, unlocking the full productivity potential of a machine. ESAB software can control and automate virtually every step of the production process to ensure fast, accurate, and easy operation. The Vision T6 also controls common gantry accessories, including the DMX automated plasma beveler, automatic drilling systems, inkjet, pin stamp or plasma marking stations. It can also control torches for cutting tubes, pipes and domes, cut with the waterjet and laser processes, and control accessories for primer removal by blasting or grinding.
Built-in Features
The new controller has a built-in RFID tag reader, which allows individual operators to log-in/log-out for simple control of permissions and traceability. A built-in Process Database with a graphical selector makes plasma or oxyfuel process set-up quick and easy. It simplifies the set-up by automatically setting parameters such as cutting speed, kerf offset, and timers based on material thickness, type, and cut quality needed. Also built-in is the EasyShape Part Program Generator which includes 88 pre-designed variable shapes and allows for DXF and DWG import and automatically adds lead-ins, lead-outs, and small hole technology where applicable.