Collets, Guide Bushings for Nomura Swiss-style Machines
Collets, Guide Bushings for Nomura Swiss-style Machines
Hardinge Workholding has announced two additional Swiss families as a standard product. Available for immediate sale are collets and guide bushings to support Nomura's line of Swiss-style turning machines, as well as six popular long bearing carbide guide bushings.
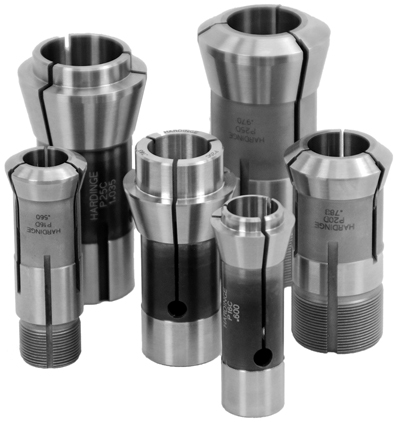

Hardinge Workholding has announced two additional Swiss families as a standard product. Available for immediate sale are collets and guide bushings to support Nomura's line of Swiss-style turning machines, as well as six popular long bearing carbide guide bushings.
Now available, P16C, P20C and P25C collets along with the corresponding P16D, P20D and P25D guide bushings for the Nomura line of CNC Swiss turning machines. Designed and engineered as a standard product by Hardinge Workholding, these products are available in round, hexagon and square sizes. This line of collets and guide bushings will cover nearly all models of Nomura's Swiss-style turning machines.
Also, available as a standard products are popular long bearing carbide guide bushings, including TD25, TD25S, TD26, TD32, TD32S and 0201 that were previously special order. Round long bearing guide bushings are carbide lined to keep the stock clean and unmarked. The extended length carbide provides additional contact surface required for longer parts.
Ryan Ervin, Manager of North American Workholding Sales and Product Development comments, "Adding new products into our standard product offering now gives our customers the opportunity to obtain the Workholding they require in 10 days or less at a competitive price. Hardinge will continue to grow our Swiss Workholding product line to meet customer demands without compromising our best in class quality or customer service.