5-axis simultaneous machining
5-axis simultaneous machining
The UMILL 1000 from EMCO is a 5-axis machining center with milling/turning, 1000mm diameter, 600mm height, 1000kg capacity, and direct drives for high precision. With the UMILL 1000, EMCO is expanding its range of universal machining centers in the 5-axis simultaneous machining sector, thereby creating a bridge between the UMILL 750 and UMILL 1500 models.
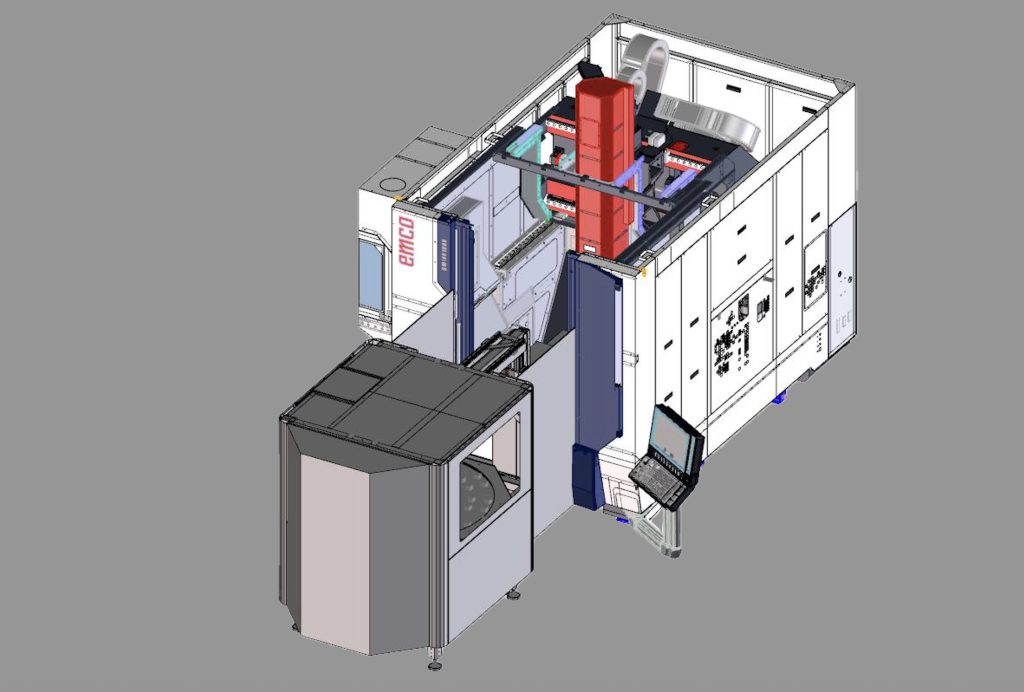
The UMILL 1000 from EMCO is a 5-axis machining center with milling/turning, 1000mm diameter, 600mm height, 1000kg capacity, and direct drives for high precision.
With the introduction of the new UMILL 1000, EMCO is expanding its range of universal machining centers in the 5-axis simultaneous machining sector, thereby creating the ideal bridge between the UMILL 750 and UMILL 1500 models. The new model was developed meet the growing demand for versatile, compact and powerful solutions that combine milling and turning operations in a single machine, opening almost unlimited application possibilities.
The highly rigid portal structure made of cast iron and welded steel ensures optimum thermal stability and enables combined turning and milling operations on a single machine. Thanks to the 55 mm roller guides on the X and Y axes and the standard direct drives in the linear axes and torque drives in the A and C axes, this universal machining centre guarantees precise machining even with demanding workpieces. With generous travel distances (900 mm in X, 1,000 mm in Y and 700 mm in Z), a large swivel range of the A-axis (± 125°) and a load capacity of up to 1,000 kg.
The motor spindle with 15,000 rpm and a maximum torque of 138 Nm at a power output of 38 kW, standard with HSK-A63, enables effective material removal and perfect surfaces.
The tool magazine of the UMILL 1000 comes standard with 30 positions and can be expanded to 60 or 90 stations if needed, with quick change and random management to optimise time and ensure greater operating autonomy. Other magazine variants are available on request.
Despite the large travel distances, the design remains modular and compact, enabling complex workpieces with a diameter of up to 1,000 mm, a height of up to 600 mm and a weight of up to 1,000 kg to be milled and turned reliably in a single clamping. The ergonomic design and numerous customization options of the UMILL 1000 enable easy integration of automation, optimal chip disposal management, and user-friendly maintenance - essential factors in intensive production environments for future-oriented companies.
Thanks to the standard glass scales in the linear axes and the direct position measuring systems in the rotary axes, Umill 1000 guarantees minimal tolerances and excellent surface quality. The direct drives in the X and Y axes enable high acceleration performance (6 m/s2) and fast feed speeds (50 m/min), thus guaranteeing maximum precision and high dynamics.
The UMILL 1000 is available with control technology from Siemens (Sinumerik ONE) or Heidenhain (TNC7). The control system is mounted on an ergonomic, forward-tilting and swivelling control panel. This solution creates optimal working conditions for the operator.





