VpCI-371 Coating
VpCI-371 Coating
Cortec VpCIs offer a range of innovative options for reducing manufacturing costs and corrosion. In the case of VpCI-371, Cortec's protection reportedly rivals the corrosion resistance of stainless steel while significantly reducing material costs.
Cortec VpCIs offer a range of innovative options for reducing manufacturing costs and corrosion. In the case of VpCI-371, Cortec's protection reportedly rivals the corrosion resistance of stainless steel while significantly reducing material costs.
VpCI-371 is a high-temperature aluminum solventborne silicone coating that provides corrosion resistance on metal substrates. It will dry tack free to 5B hardness in about 20 minutes at room temperature and will achieve 9H hardness after heating. This is an ideal coating for applications that will reach high temperatures because the coating is heat stable to 1200° F with prolonged heat resistance from 400-1200° F.
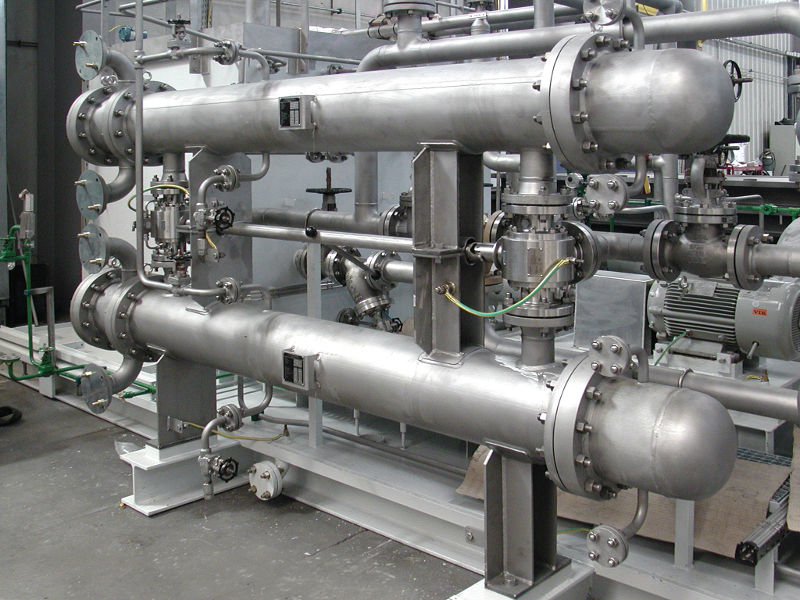
VpCI-371 turned out to be just the high-temperature coating a manufacturer of oil coolers was looking for as it tried to reduce the high cost of using stainless steel while maintaining corrosion resistance. The company manufactures hundreds of oil coolers for a major producer of heavy equipment. When carbon steel oil coolers had been used inside the heavy equipment, corrosion was found at the 6-month preventative maintenance check. Because of this, the manufacturer had to use more expensive stainless steel to make oil coolers that would resist corrosion.
However, the manufacturer wondered if a high-temperature protective coating from Cortec would allow them to make carbon steel oil coolers that would resist corrosion as well. To examine the prospect, oil coolers manufactured out of carbon steel were internally coated with VpCI-371 and sent to the field for testing. At the 6-month preventative maintenance check, no corrosion was found on the oil coolers. The heavy equipment customer agreed to specify carbon steel and VpCI-371 as the materials for making future oil coolers to install in their heavy equipment. This
resulted in a significant cost reduction to the oil cooler manufacturer, who was now able to use a cost-effective material to create oil coolers that would not corrode.





